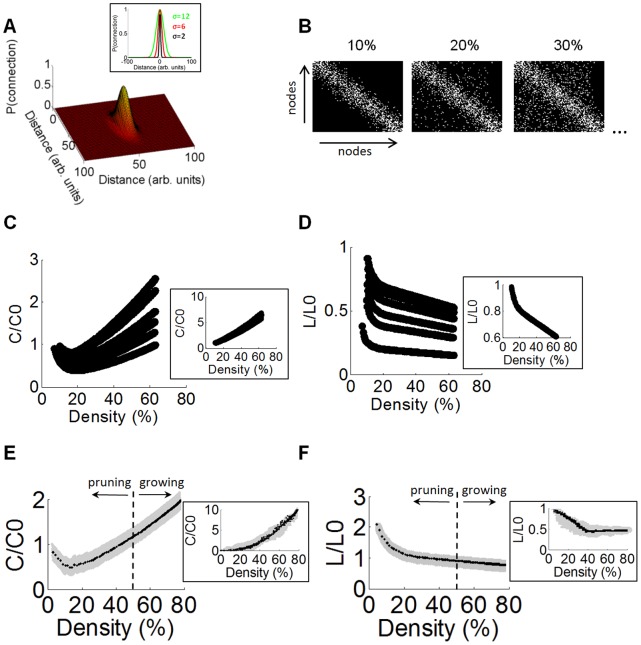
Figure 6. Spatially-embedded model of functional connectivity reproducing 4-AP/bic-induced alterations.
A. Gaussian probability density function of the relationship between physical distance (arbitrary units) and the probability of two nodes being connected in the model. Inset: three different Gaussian functions are shown, with different values of standard deviation (σ). B. Connectivity maps for three different versions of the model where the density of connections is either 10%, 20%, or 30% of the total possible number of connections. The model was composed of 100 nodes. Binary ([0,1]) connections between nodes are shown in white. All three examples were generated with σ = 6. C–D: Using a spatially-embedded model of connectivity (see Main Text), we computed mean values of clustering coefficient (C) and path length (D) obtained with different percentages of connection densities ranging from a sparse model (10% density) up to a densely connected model (70% density). Different lines show models with values of σ = 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2 (from top to bottom) controlling the standard deviation of spatial embedding. Measures of clustering and path length were normalized by random networks that preserved degree sequence [25]. Note the U-shaped relation between clustering and density, whereas path length decreases monotonically as density increases. Inset: same as C-D, but obtained from a model with no spatial embedding. E–F: DMSO networks at baseline (DIV 14) exhibit a similar U-shaped relation between clustering coefficient and density (E) as the spatially-embedded model (σ = 2), while path length (F) decreases monotonically with density. Solid black lines: mean clustering coefficient and path length taken over DMSO baseline networks. Vertical dashed line: Mean density of original DMSO networks (without growing or pruning). Shaded areas: SEM. Inset = clustering and path length in analyses with no spatial embedding of the growing and pruning processes.