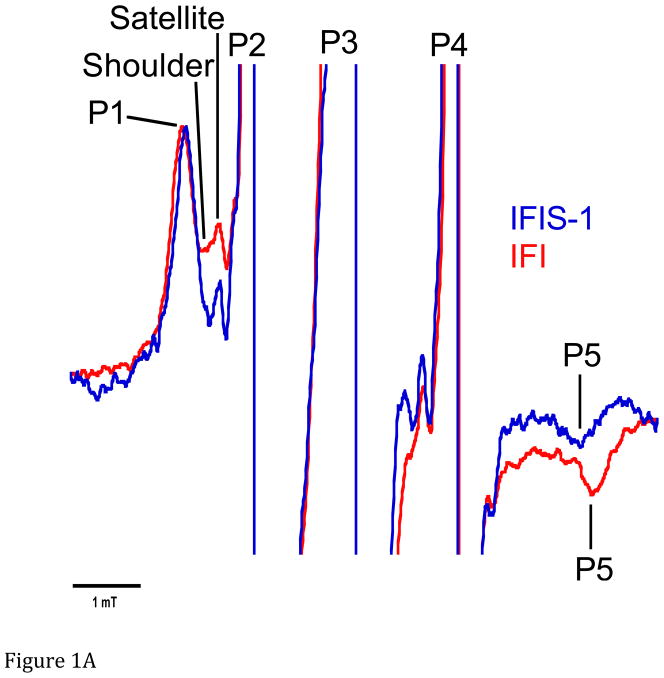
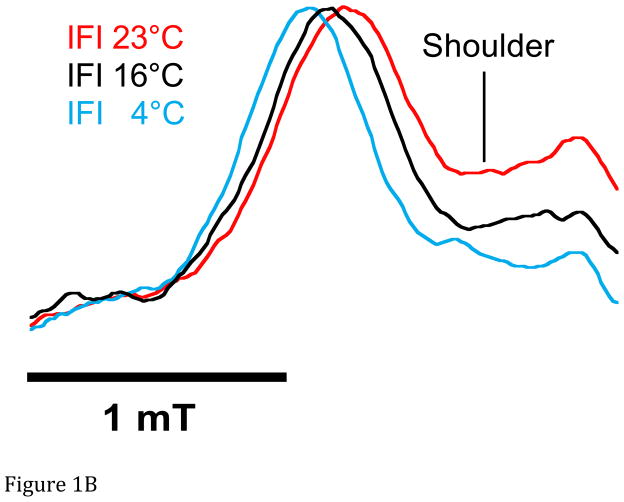
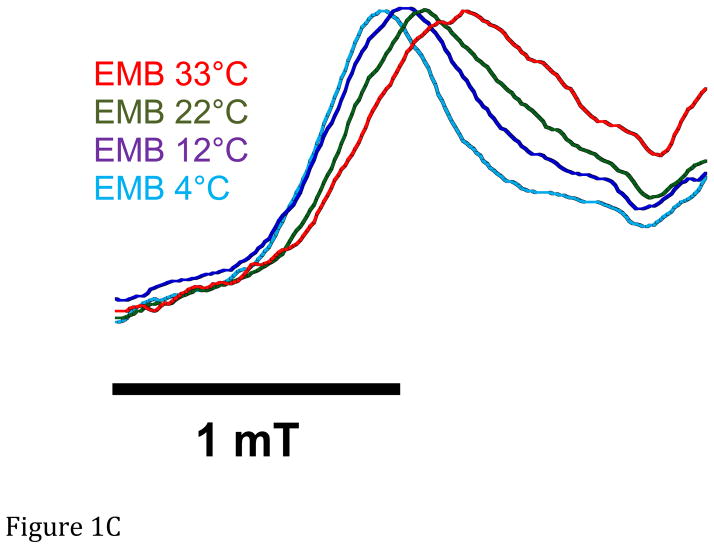
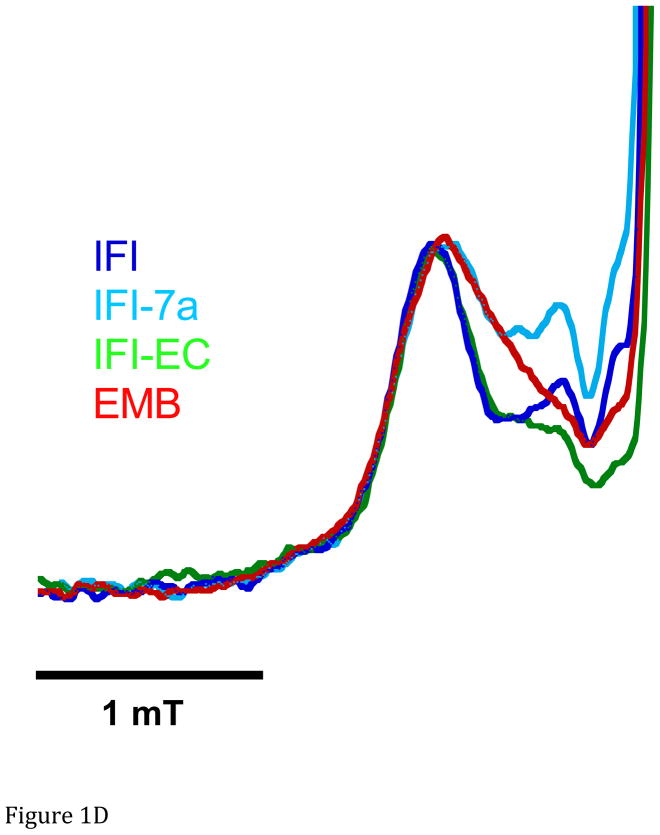
Figure 1.
A. Representative spectra of Drosophila indirect flight muscle S1 (IFIS-1) bound to 2′-SLADP (blue) and A•M•2′-SLADP bound to IFI in IFM fibers (red). Both spectra are at 23°C. The vertical axis is the derivative of absorption. The horizontal axis is magnetic field. Center field is 350.6 mT. B. Low field, P1, component of A•M•2′-SLADP bound to IFI in IFM fibers at 4°C (cyan), 16°C (black) and 23°C (red). There is a clear, high-field shoulder to the P1 component of the spectrum that changes with temperature. C. Low field, P1, component of A•M•2′-SLADP bound to embryonic myosin (EMB) in IFM fibers at 4°C (red), 12°C (blue), 22°C (green) and 33°C (cyan). D. Low field component of the A•M•2′-SLADP EPR spectrum comparing four different acto-myosin•SL-ADP complexes, IFI (blue), IFI-7a (cyan) EMB (red) and IFI-EC (green) at 23°C. All spectra are normalized to have the same magnitude for the primary peak in the P1 component.