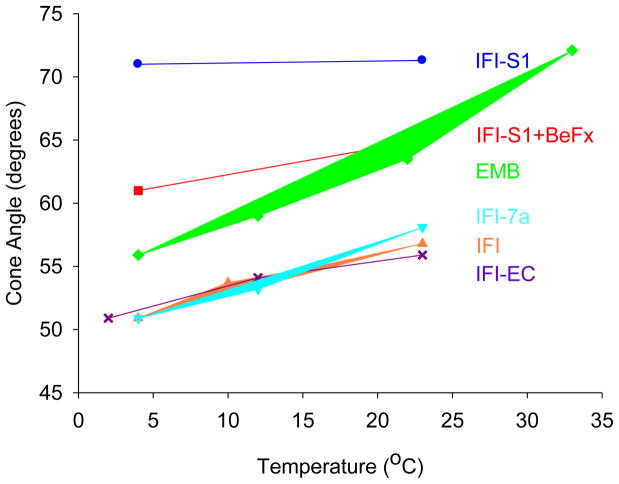
Figure 2.
Cone angles of mobility for 2′-SLADP bound to Drosophila S-1, and myosin in skinned IFM fibers as a function of temperature. Effective cone angles of mobility were approximated using the order parameter S=(T||′ − T0)/(T|| − T0) as a measure of probe mobility. 2T||′ is the observed splitting, 2T|| is the splitting for an immobilized probe (7.20 mT) and 2T0 is the isotropic hyperfine splitting for freely tumbling 2′-SLADP in solution (3.22 mT). The cone angle is then given by cos θ = −0.5+0.5*(1+8S)1/2, where 2θ is the vertex angle of the cone of mobility (Griffith and Jost 1976; Alessi et al. 1992). Each value is the mean of 1–4 distinct observations. The standard errors of the EPR cone angles are ± 0.18 degrees.