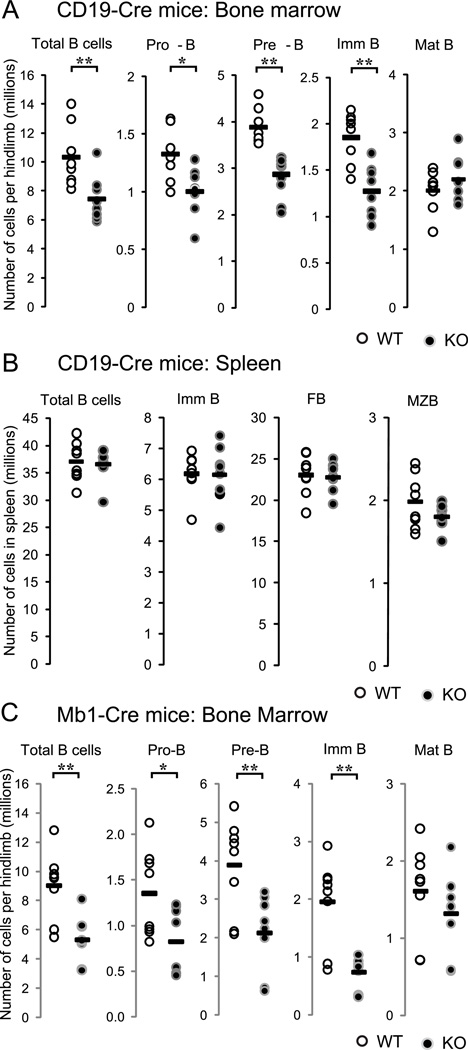
Figure 1. Selective decrease of progenitor B cell number in B cell specific FAK knockout mice.
(A) BM cells from Cd19-Cre Fak KO or WT control mice, (B) spleen cells from Cd19-Cre Fak KO or WT control mice, or (C) BM cells from mb1-Cre Fak KO or littermate WT control mice were prepared and stained with monoclonal antibodies. Total numbers of each population per limb (one femur and one tibia) or per spleen were calculated using flow cytometry analysis and automated complete blood count. Student’s t-tests were performed as shown *, P<0.05, and **, P<0.01 (unpaired, two-tailed). n=8. Dots indicate individual mice; bar indicates the mean. BM cell gates: Total B cells (B220+ CD19+), Pro-B (B220lo CD19+ IgM− CD43+), Pre-B (B220lo CD19+ IgM− CD43−), Imm B (immature B cells, B220lo CD19+ IgM+ AA4.1+), Mat B (mature B cells, B220hi CD19+ IgM+ AA4.1−); spleen cell gates: Total B (CD19+), Imm B (immature B, CD19+ CD23− CD21/35−), FB (follicular B cells, CD19+ CD23+ CD21/35mid), MZB (marginal zone B cells, CD19+ CD23−/lo CD21/35hi). Data are pooled from 4 independent experiments.