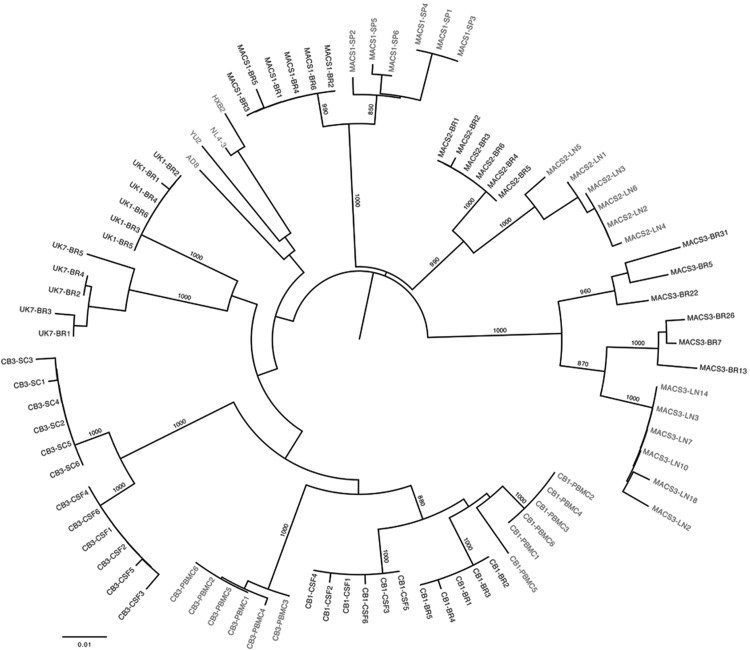
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of long terminal repeat (LTR) nucleotide sequences. The phylogenetic tree, shown in radial representation, was constructed from an LTR nucleotide multiple sequence alignment, as described previously.27 Briefly, the phylogenetic analysis was performed using the neighbor-joining algorithm of MEGA 4 (MEGA Software, Tempe AZ), with a transition/transversion ratio of 2.0, empirical base frequencies, and a randomized input order of sequences. A consensus tree was generated from bootstrapping of 1,000 replicates, which was viewed in FigTree to produce the final figure (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/). Clone names for central nervous system (CNS)-derived LTRs are shown in black and non-CNS-derived LTRs are shown in gray. The nucleotide sequences of HIV-1 AD8, YU2, NL4-3, and HXB2 LTRs are shown in gray and were included for comparison. Numbers associated with each branch are bootstrap values obtained from 1,000 replicates. Only values above 700 for the major branches are shown. Branch lengths are proportional to the amount of sequence divergence. The scale bar represents 1% genetic distance.