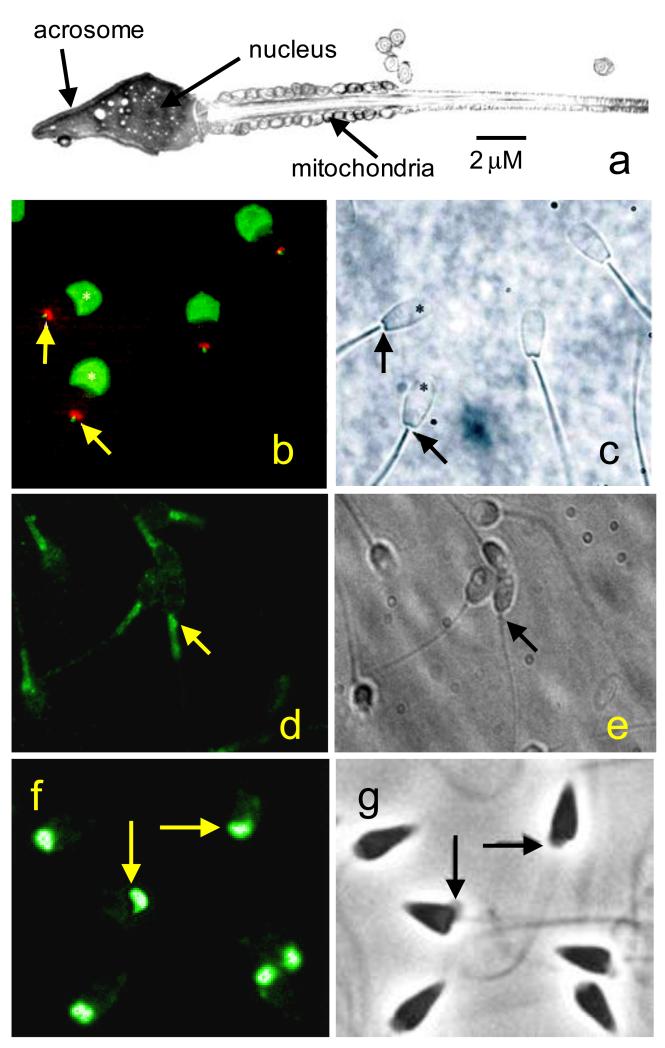
Figure 1.
Localisation of Ca2+ store components in sperm. a; Electron microscope image of a human sperm showing the localisation of the acrosome, nucleus and mitochondria. b: immunolocalisation of InsP3Rs (green) and nuclear pore complex proteins (red) in bovine sperm. InsP3 receptors are localised over the acrosome (asterisks) and also at the sperm neck (arrows). Nuclear pore complex proteins indicate site of redundant nuclear envelope. c: phase image of the cells in panel b. d: immunolocalisation of secretory pathway Ca2+ ATPase (SPCA) (green) in human sperm. SPCA is restricted to the neck and midpiece. In many cells there is a particular concentration at the sperm neck (arrows). e: phase image of the cells in panel d. f: immunolocalisation of secretory pathway Ca2+ ATPase (SPCA) (green) in sperm of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. SPCA localises to the giant mitochondrion in each cell (arrows). g: phase image of the cells in panel f. Panels b and c from Ho and Suarez (2003) with permission. Panels f and g from Gunaratne & Vacquier (2006) with permission.