Figure 4.
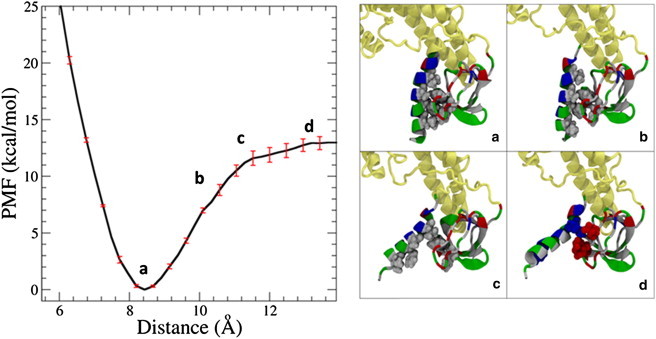
The binding energy of the H0/SH3 complex in the full endophilin protein is 13.0 ± 0.6 kcal/mol, on the order of several hydrogen bonds. (a) The stability of the complex is driven by the hiding of the hydrophobic residues on both domains from the solvent. (b) As the distance is increased between the helix and the SH3 domain, more hydrophobic residues are exposed to the solvent, and the structure becomes less energetically stable. (c) Eventually, the hydrophobic residues on both structures are fully exposed to the solvent, leading to an unfavorable structure. (d) A further increase in distance leads to some transient salt-bridge formation, until there is no interaction between either of the domains. The proteins are represented here using the New Cartoon and van der Waals representation. The BAR domain and linker are colored tan and the H0/SH3 complex is colored according to residue type (hydrophobic residues are white, polar residues are green, acidic residues are red, and basic residues are blue).
