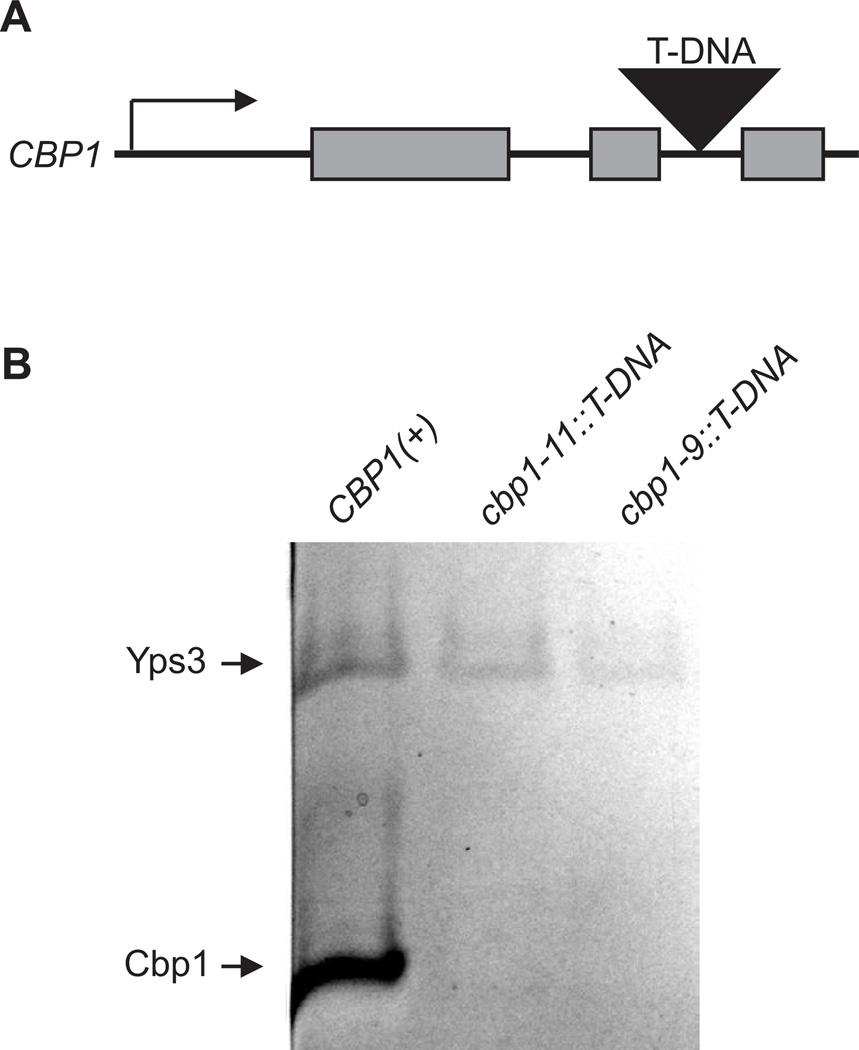
Figure 3. T-DNA integration into introns is sufficient to disrupt genes.
(A) Schematic showing the location of the T-DNA integration between the second and third introns of the CBP1 gene. The T-DNA element for mutant allele cbp1-11::T-DNA (strain OSU128) is located 28 base pairs from the end of the 2nd exon and 29 base pairs from the start of the 3rd intron. (B) Production of the 10 kDa Cbp1 protein by wild type and T-DNA insertion lines. Equivalent volumes of culture filtrate from CBP1(+) (strain WU15), and two mutant cbp1 lines were separated by SDS-PAGE and the extracellular proteins visualized by silver staining. The identity of the Cbp1 protein band was verified by its absence from culture filtrate derived from the cbp1-9::T-DNA mutant (strain OSU8), a previously characterized line in which T-DNA insertion in the CBP1 promoter prevents expression of the CBP1 gene (Youseff et al. 2009). The 18 kDa Yps3 protein band was used to validate equivalent amounts of culture filtrate were analyzed.