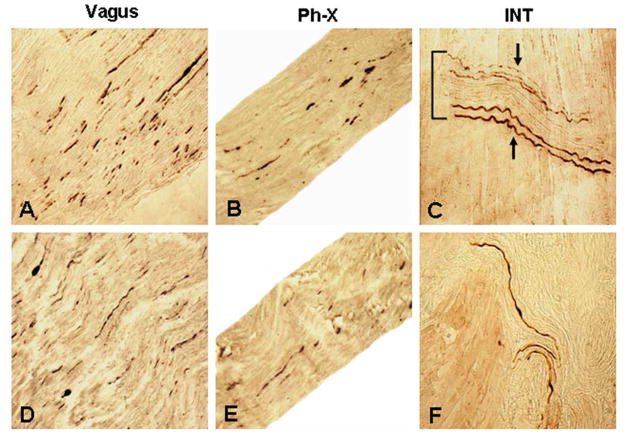
FIGURE 2.
Photomicrographs of the longitudinal sections of cervical X nerve trunk (A, D), pharyngeal branch of the X nerve (Ph-X) (B, E), and pharyngeal muscles (C, F) immunostained for phosphorylated α-synuclein (psyn) in PD subjects with dysphagia (A–C) and without dysphagia (D–F), showing Lewy neurites (LNs) in the nerves examined and immunoreactive intramuscular nerve twigs (INTs) in the muscles. (A) A stained section of a cervical X nerve trunk from a PD subject with dysphagia (PD 3, 78-year-old man with disease duration of 19 years, Hoehn & Yahr 4, and motor UPDRS 51; lesion severity: severe, +++). Note that there were numerous LNs (darkly stained threads and dots) in the X nerve. x200. (B) A stained section of the Ph-X from the same PD subject as in A. Note that the Ph-X in this case also contained frequent LNs (lesion severity: moderate, ++). x200. (C) A stained section of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor (IPC) from the same PD subject as in B. Note that an INT running across the muscle fibers was horizontally sectioned. Several axons on the superior and inferior margins of the INT were positively immunostained with anti-psyn immunohistochemistry (arrows), whereas the normal axons in the center of the INT remained unstained. x200. (D) A stained section of cervical X nerve trunk from a PD subject without dysphagia (PD 9, 80-year-old man with disease duration of 17 years, Hoehn & Yahr 5, and motor UPDRS 40; lesion severity: moderate, ++), showing frequent LNs in the X nerve. x200. (E) A stained section of the Ph-X from the same PD subject as in D. Note that there were several LNs in the Ph-X (lesion severity: mild, +). x200. (F) A stained section of cricopharyngeal (CP) sphincter from the same PD subject as in E, showing three immunoreactive axons in the muscle. x200.