Fig. 3.
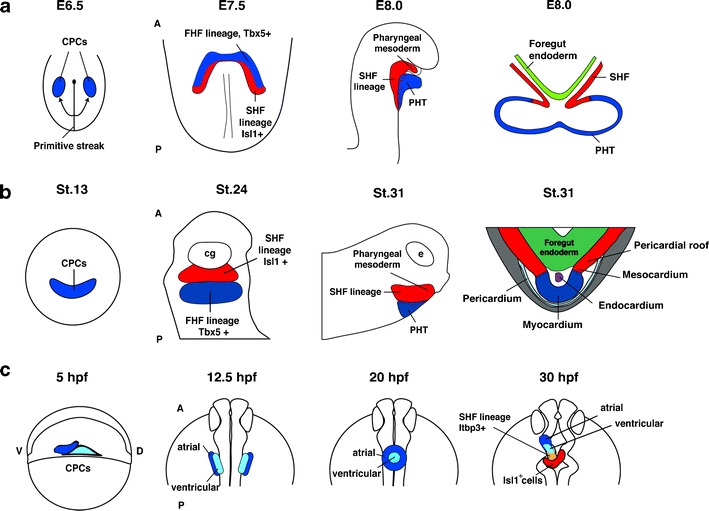
A simplified schematic presentation of heart development in different species. a Mouse. Developmental stages are indicated in embryonic days (E). The cartoons show a dorsal view of a flattened embryo (E6.5), an anterior view (E7.5), and a lateral view (E8.0). Additionally, a schematic illustration of a transverse section at E8.0 is provided. The SHF is characterized by the presence of Isl1-positive cells and is indicated in red. b X. laevis. Developmental stages are according to Nieuwkoop and Faber (1975). The cartoons show an anterior view (st.13), a ventral view (st.24), and a lateral view (st.31). Additionally, a schematic illustration of a transverse section through the heart at st.31 is provided. At st.24, cells of the SHF (red) express isl1 whereas cells of the FHF (blue) are positive for tbx5. c D. rerio. Developmental stages are indicated in hours post-fertilization (hpf). The cartoons show a lateral view for stage 5 hpf and dorsal views for stages 12.5, 20, and 30 hpf with the anterior side up. The localization of early cardiac progenitor cells at 40 % epiboly, as well as the distinction between an atrial and a ventricular fate was analyzed by fate-mapping experiments. An Isl1-positive cell population that contributes to the arterial pole is located posterior and dorsal to the ventricle and is indicated in red. It only partially contributes to the heart. The zebrafish SHF is characterized by the expression of ltbp3. Of note, the arrangement of the atrium and ventricle along the anterior–posterior axis is inverted at later stages (not shown here). As a result, the atrium will come to lie posterior to the ventricle. CPC: common cardiac progenitor cell population, A: anterior, D: dorsal, P: posterior, V: ventral, FHF: first heart field; SHF: second heart field, PHT: primary heart tube. Partly adopted from Gessert and Kühl (2009)
