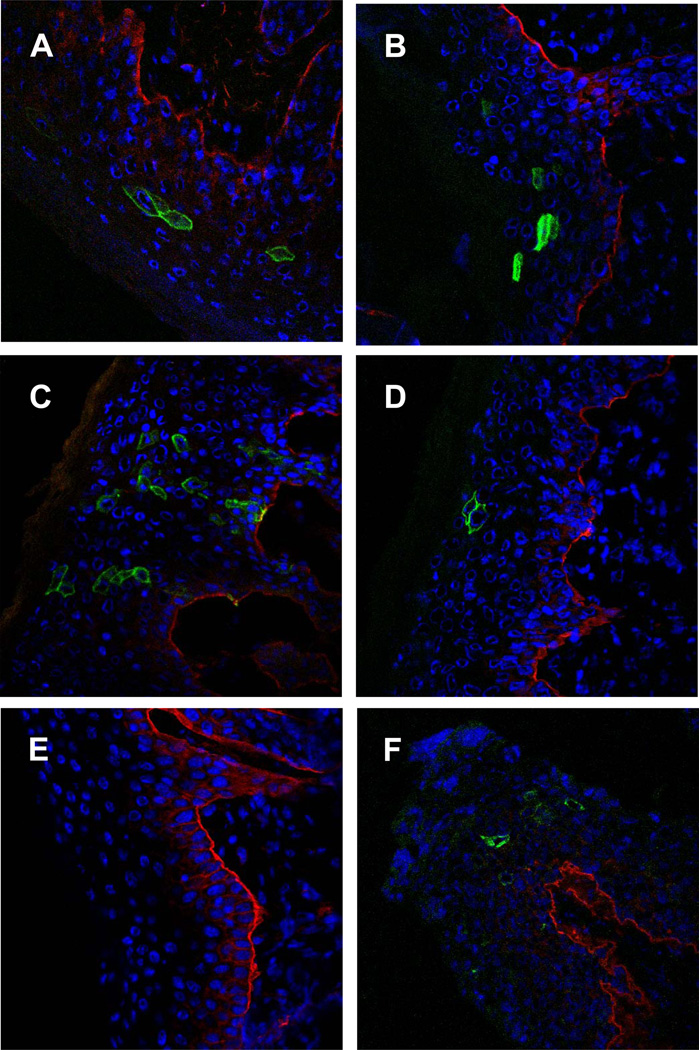
Fig. 2.
Cellular distribution of pseudogenome expression for representatives of different human and animal papillomavirus types in the (A–E) skin and in (F) genital tissues, visualized by immunofluorescent staining and confocal microscopy. All pseudovirions encapsidated the reporter gene plasmid pNaMB, which encodes a non-signaling “tailless” human CD4 reporter gene. Detection was performed using an antibody specific for human CD4 followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). To determine the localization of infected cells in relation to the basement membrane, co-staining was performed with an anti-CD49f (integrin alpha 6) phycoerythrin-labeled antibody (red). Skin samples (A–E) were analyzed on day three, genital tissues (F) on day two after infection. The representatives of human and animal papillomaviruses are as follows: (A) cutaneous HPV 5, (B) mucosal HPV 16, (C, F) mouse papillomavirus and (D) bovine papillomavirus 1. (E) Skin tissues of control mice that were mock-treated with phosphate-buffered saline.