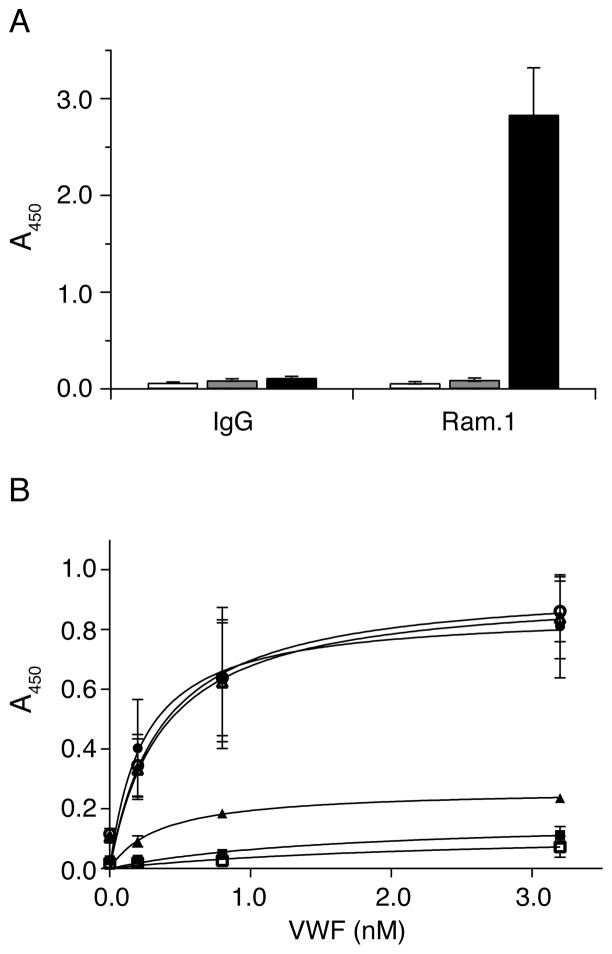
Figure 5. Effect of RAM.1 on the VWF-binding activity of GPIb-IX reconstituted in Nanodiscs.
(A) The binding of RAM.1 to GPIb-IX in Nanodiscs. 2 μg/ml rat IgG or RAM.1 was incubated with immobilized GPIb-IX/ND (■) or empty Nanodiscs (
 ) or BSA (□) and the binding was detected by HRP-conjugated goat anti-rat antibody. (B) The effect of RAM.1 on botrocetin-induced VWF binding to GPIb-IX in Nanodiscs. 10 μg/ml antibodies, rat IgG (○) and RAM.1 (●), mouse IgG (△) and AK2 (▲) were pre-incubated with GPIb-IX/ND-coated wells, and then increasing concentrations of VWF with 0.2 U/ml botrocetin was added. The binding was detected by HRP-conjugated anti-VWF antibody. The addition of VWF with botrocetin to empty Nanodiscs- (■) or BSA- (□) coated wells served as negative controls. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured from 3 independent experiments and presented as the mean ± SD. For some data points, their error bars are smaller than the symbols.
) or BSA (□) and the binding was detected by HRP-conjugated goat anti-rat antibody. (B) The effect of RAM.1 on botrocetin-induced VWF binding to GPIb-IX in Nanodiscs. 10 μg/ml antibodies, rat IgG (○) and RAM.1 (●), mouse IgG (△) and AK2 (▲) were pre-incubated with GPIb-IX/ND-coated wells, and then increasing concentrations of VWF with 0.2 U/ml botrocetin was added. The binding was detected by HRP-conjugated anti-VWF antibody. The addition of VWF with botrocetin to empty Nanodiscs- (■) or BSA- (□) coated wells served as negative controls. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured from 3 independent experiments and presented as the mean ± SD. For some data points, their error bars are smaller than the symbols.