Fig. 5.
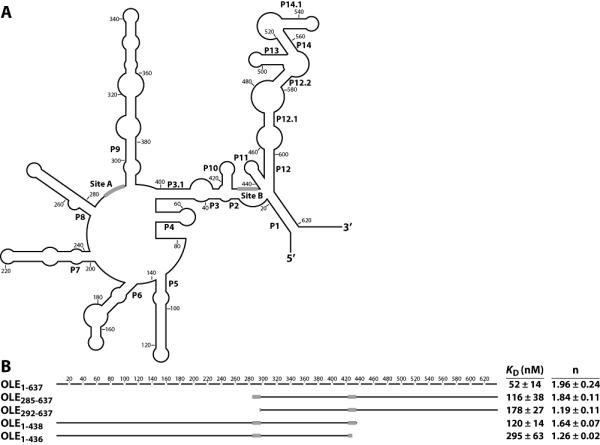
Identification of nucleotides necessary for formation of the OLE-OAP complex. (A) Secondary structure of the B. halodurans OLE RNA sequence is depicted in outline. Black bars indicate the predicted OAP binding sites as determined in B. (B) Full-length OLE RNA is depicted as a broken line, with each line segment corresponding to 20 nucleotides. Solid lines correspond to the indicated truncated constructs, with approximate location depicted graphically. The KD and Hill coefficient for each construct were calculated from at least four experiments and are given with the standard error. From these truncations, predicted OAP-binding sites were identified and depicted as black boxes on both the truncated RNAs and in part A. No binding (n.b.) was observed for the construct OLE285-438.
