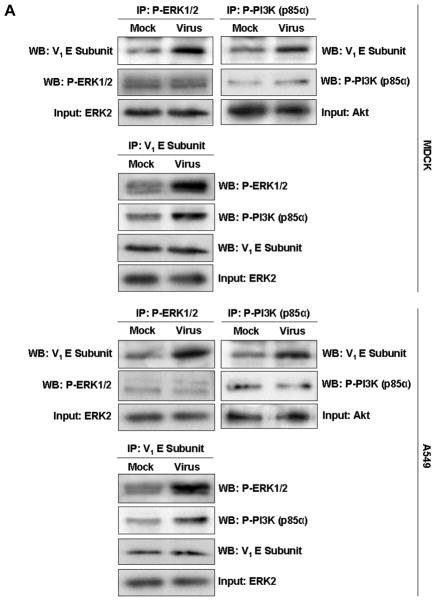
Fig. 4. The V-ATPase V1 domain subunit E interacts with ERK and PI3K in influenza A virus-infected cells.
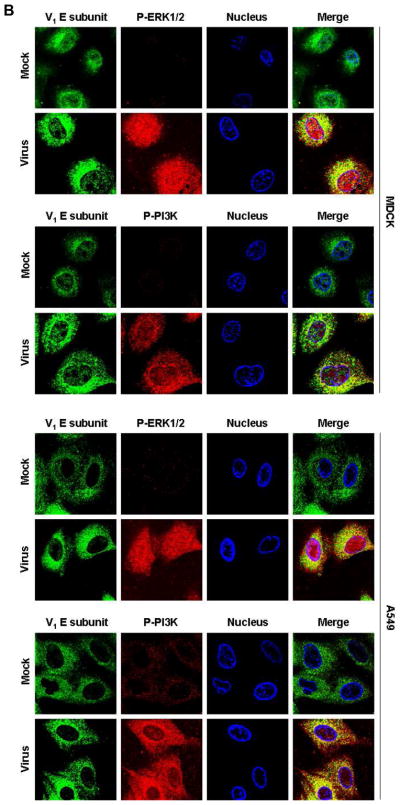
(A) V-ATPase was immunoprecipitated from MDCK or A549 cell lysates 60 min after addition of PR/8 (MOI = 5) with antibodies specific for the phosphorylated form of ERK1/2 (P-ERK1/2) or PI3K (P-PI3K p85α) (upper panels), and P-ERK1/2 and P-PI3K p85α were immunoprecipitated with antibody to subunit E of the V-ATPase V1 (lower panels). Co-immunoprecipitated products were analyzed by Western blotting. Equal protein loading of P-ERK1/2, P-PI3K and V1 E subunit was verified by Western blots using the respective specific antibodies. (B) Colocalization of V-ATPase V1 subunit E (green) with P-ERK1/2 and P-PI3K p85α (both shown in red) 60 min after addition of PR/8 (MOI = 5). Merged images show colocalization of V1 E subunit with P-ERK1/2 or P-PI3K. Magnification 63x.