Fig. 2.
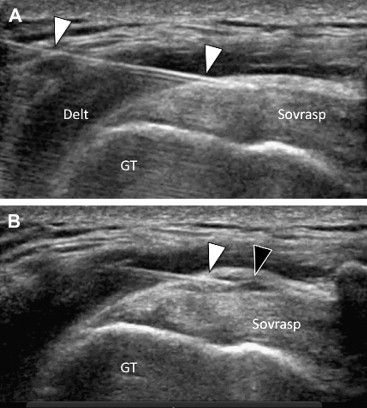
Shoulder: Lateral infiltration of cortisone and anesthetic in the subacromial bursa. A) US image, performed in the coronal oblique plane, shows the 22-Gauge needle (white arrowheads) situated between the deltoid muscle (Delt) and the supraspinatus tendon (sovrasp). The needle tip is perfectly positioned in the subacromial bursa showing wall thickening and absence of internal fluid collection. B) After US-guided injection of a few drops of solution, the injected solution is visible (black arrowhead) in the form of a small anechoic fluid collection situated inside the bursa. GT = greater tuberosity of the humerus.
