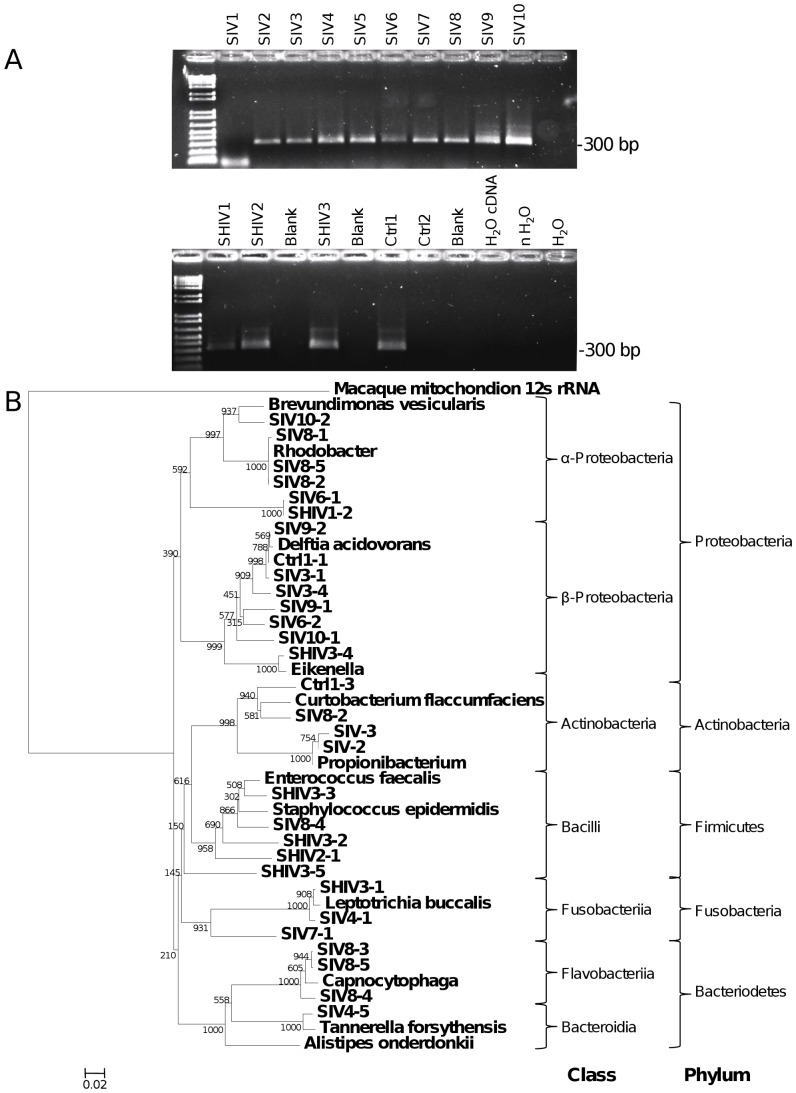
Figure 5. 16 s rRNA sequences from brain-derived cDNA of cynomolgus macaques.
(A) Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel showed the amplicon generated by primers 16 s514F and 16 s 806R from SIV-infected macaques 1–10, SHIV-infected macaques 1–3 and FIV-challenged macaque 1 and 2. cDNA synthesized with ultrapure water, water carried through both rounds of nested PCR and water used as template only in the final round of PCR were all included as negative controls. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of 16 s rRNA region sequences amplified by the primers 514F and 806R derived from macaque brain specimens. Clustal alignments were generated comparing amplicon sequences with the equivalent position of published 16 s rRNA sequences identified by BLAST analysis. The Neighbor joining tree was generated based on 10,000 bootstrap trials and rooted on the macaque mitochondrial 12 s rRNA sequence. Again, these data showed a predominance of Proteobacteria in brain-derived 16 s rRNA clones although other bacteria, e.g., Actinobacter and Bacilli, were detected.