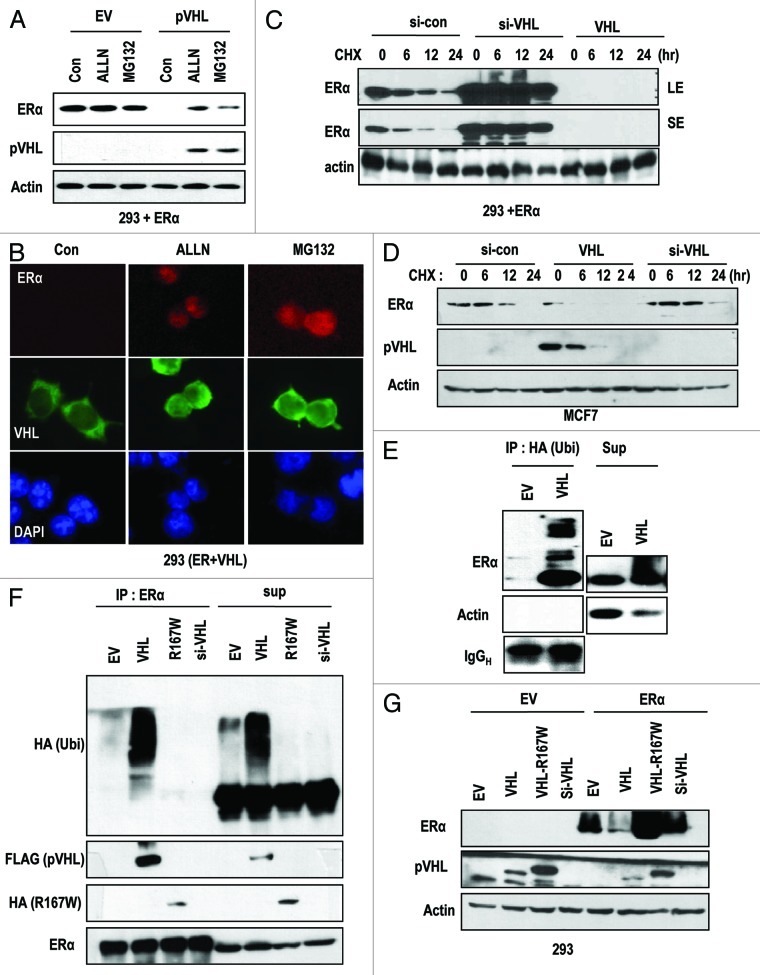
Figure 2. pVHL promotes ER-α degradation through an E3 ligase. (A) Blocking of proteasomal degradation induces ER-α expression. Two hundred and ninety-three cells were transfected with the indicated vectors or si-RNAs for 24 h and were treated with ALLN and MG132 (50 μg/ml) for 6 h. SE and LE indicate short exposure and long exposure. (B) Proteasome inhibitors block pVHL-induced reduction in nuclear ER-α. 293 cells were co-transfected with VHL and ER-α for 24 h and incubated with ALLN or MG132 for 6 h. After fixation with Me-OH, 293 cells were stained with anti-ER-α (red), anti-pVHL (green) and DAPI (blue). (C) si-VHL extends the half-life of ER-α. Two hundred and ninety-three cells were co-transfected with ER-α and si-VHL or pVHL for 24 h. To block de novo synthesis, cycloheximide (CHX; 5 μg/ml) was added for the indicated times. Although VHL transfection completely eliminated ER-α, si-VHL extended the ER-α half-life. LE and SE indicate a long exposure and a short exposure, respectively. (D) pVHL can reduce the half-life of ER-α. MCF7 cells were transfected with the indicated vectors or si-RNAs for 24 h. After washing with serum-free medium, de novo synthesis was blocked by cycloheximide treatment for indicated times, and the expression of ER-α was measured. (E and F) ER-α is ubiquitinylated through the E3 ligase activity of pVHL. Immunoprecipitation was performed using HA or ER-α antibodies, and the co-precipitated proteins were analyzed using the indicated antibodies. Whole-cell extracts were obtained from 293 cells transfected with the indicated vectors. (G) ER-α can be suppressed by wild-type but not mutant pVHL. Two hundred and ninety-three cells were transfected with the indicated vectors or si-RNAs for 24 h.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.