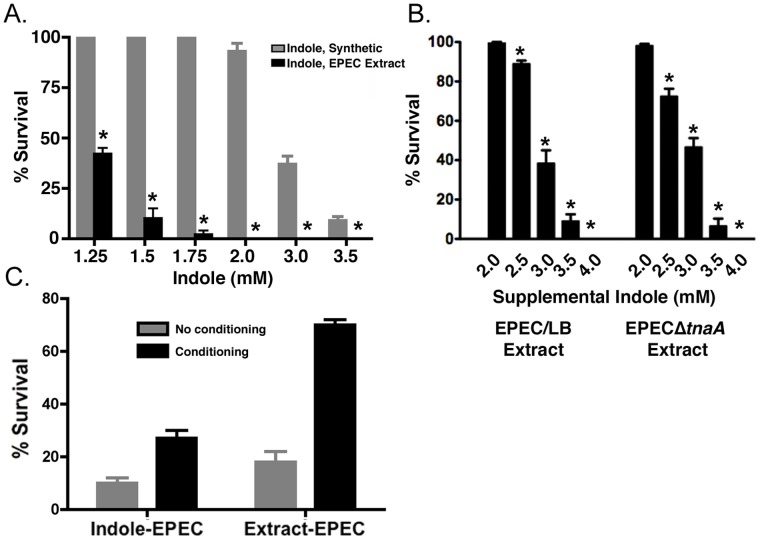
Figure 3. Effects of synthetic indole or extract on killing and conditioning of C. elegans.
(a) Comparison of the effect of synthetic indole or of EPEC agar extracts in which the indole concentration has been estimated based on HPLC measurements of the indole concentration in identically prepared samples. Note that the LD90 for synthetic indole is 3.5 mM, but that the extract kills even at indole concentrations of 1.5 mM, suggesting that additional factors in the extract contribute to killing. Mean +/− SEM are shown; * corresponds to p<0.001 with respect to control at each dilution. (b) Tryptophan and tryptophanase are required for production of additional killing factors. N2 worms were exposed either to EPEC extracts from LB plates lacking tryptophan or to EPECΔtnaA extracts. Significant killing was evident in either condition only when synthetic indole was added at concentrations greater than 3 mM. Mean +/− SEM are shown; * corresponds to p<0.01 with respect to control at each dilution. (c) Comparison of the effects of conditioning C. elegans with either 3.5 mM indole or with extract derived from EPEC/LBT plates, and challenging with EPEC. Note that extract conditions 2-fold better than indole. Mean +/−95% confidence intervals are shown. Lack of overlapping error bars indicates significance at the 5% level.