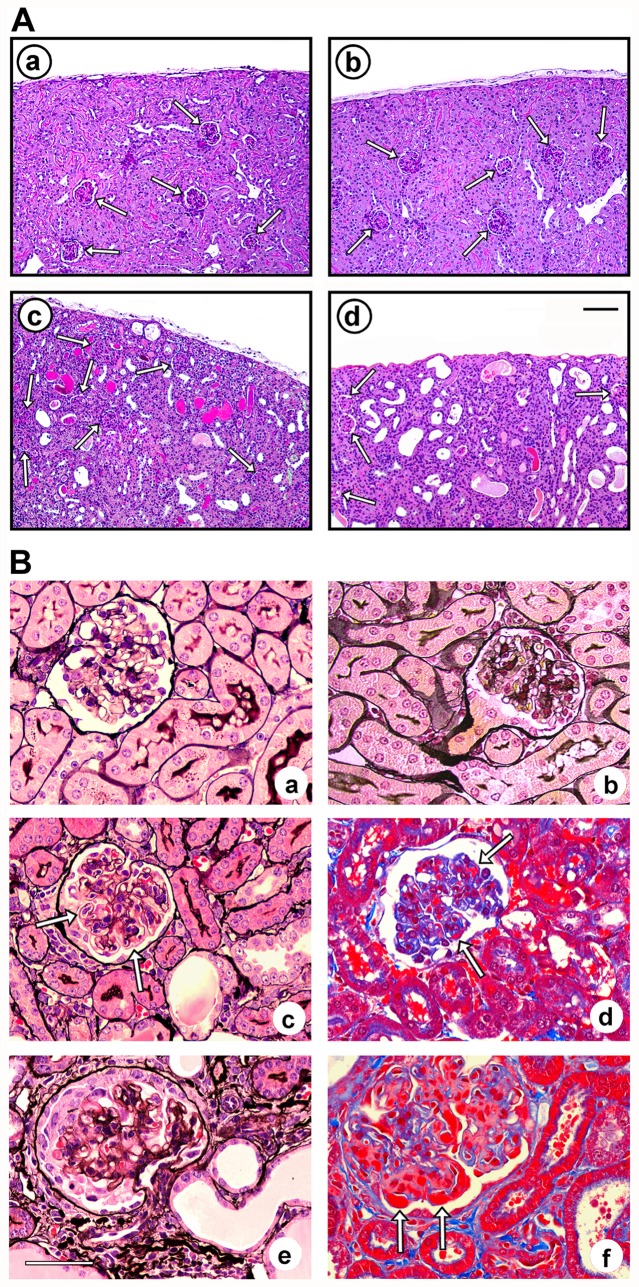
Figure 4. Cortical morphological lesions from wild-type and MK2/MK3 knock-out mice in response to the AMC serum.
Kidney sections from untreated and AMC serum-treated wild-type mice (MK2+/+MK3+/+), MK2/MK3 double knock-out mice (MK2−/−MK3−/−), and MK3 knock-out mice (MK2+/+MK3−/−) on day 16 are shown. (A) Periodic acid-Schiff stain of the renal parenchyma of wild-type (panels a, c) and MK2/MK3 double knock-out mice (panels b, d), left untreated (panels a, b) or treated with the AMC serum (panels c, d). Normal morphology of the renal parenchyma was noted in untreated mice of both genotypes. Renal injury in response to the AMC serum included dilation of renal tubules and the presence of hyaline casts. Arrows designate glomeruli. Scale bar: 100 µM. (B) Silver stain (panels a–c, e) and trichrome stain (panels d, f) of glomeruli from untreated wild-type (panel a) and MK2/MK3 double knock-out mice (panel b), and from AMC serum-treated MK2/MK3 double knock-out (panels c–e) and MK3 knock-out mice (panel f). A preserved glomerular morphology was noted in untreated wild-type and MK2/MK3 double knock-out mice. Glomerular injury in response to the AMC serum included a thickening of the capillary walls due to duplication of basement membranes (tram-tracking) with associated mesangial interposition and narrowing of the capillary lumina (panel c, arrows), small fuchsinophilic subendothelial and mesangial deposits (panel d, arrows), and necrotizing lesions with associated crescent formation (panel e). These lesions were noted in mice of all genotypes. In addition, large, wire-loop type subendothelial deposits were found in the MK3 knock-out mice (panel f, arrows). Scale bar: 50 µM.