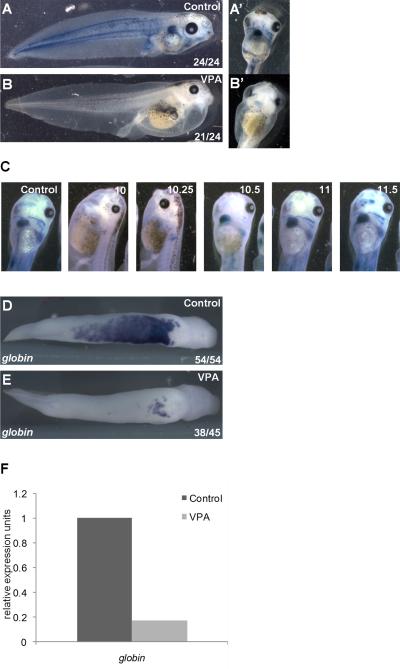
Figure 1. HDAC inhibition blocks primitive erythropoiesis in Xenopus laevis.
A) Circulating RBCs visualized in tadpoles (stage 43) by benzidine staining (blue) for hemoglobin. RBCs are also present in pronephros (arrow) and in heart (A’, ventral view). B) Treatment of gastrulating embryos (stage 10-12) with the class I HDAC inhibitor VPA blocks blood formation, indicated by benzidine staining (B’, ventral view). C) Numbers indicate stages during gastrulation at which VPA was administered; in all conditions, VPA was removed at the end of gastrulation (stage 12). Benzidine positive RBCs are readily visible within the heart and great vessels in controls and when VPA was added at stage 10.5 or later. D,E) Expression of the erythrocyte marker alpha-T1 hemoglobin in the VBI detected by WISH in tailbud embryos (stage 31). In VPA treated embryos (E), globin expression is dramatically reduced, with residual staining restricted to the aVBI. F) Embryos were treated with control buffer or VPA during the gastrula stage and globin expression in stage 28 embryos was assessed by quantitative RT-PCR.