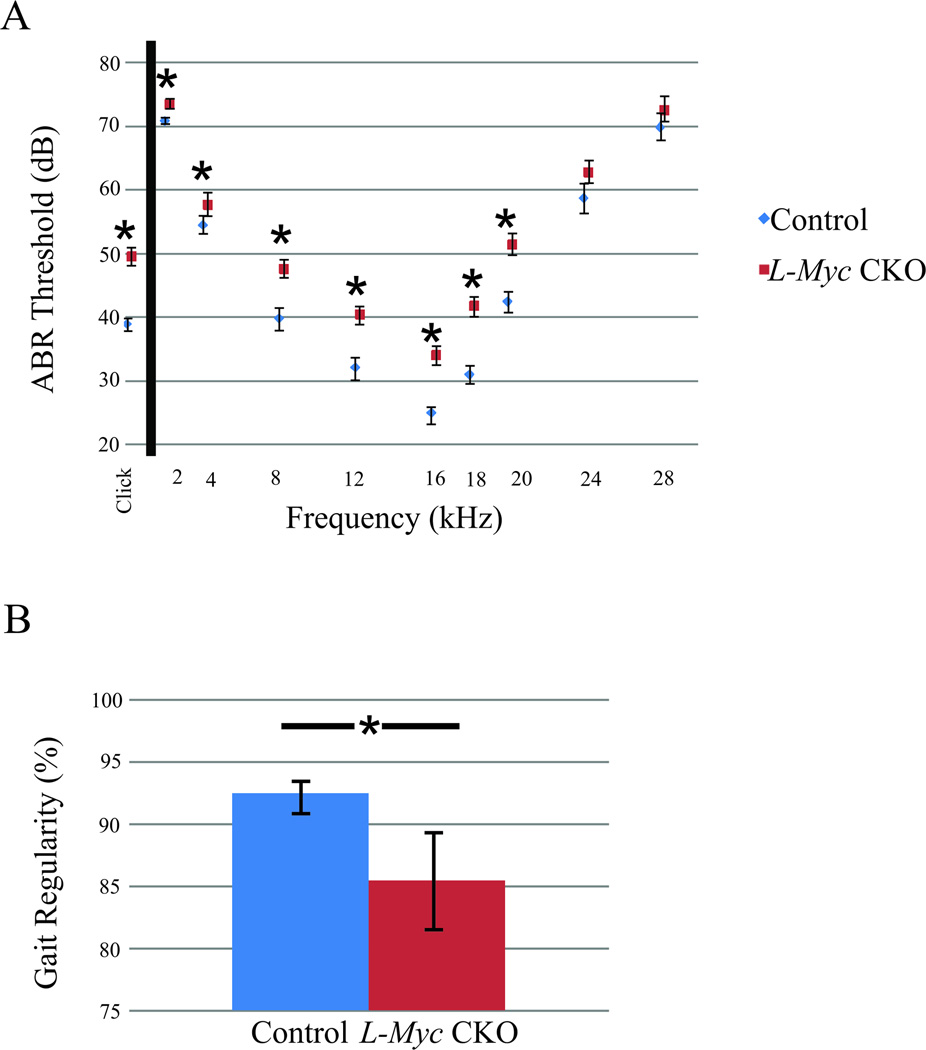
Figure 5. Loss of L-Myc results in some auditory and vestibulo-motor abnormalities.
Auditory and vestibulo-motor functions are assessed using the ABR threshold and by the Catwalk system for the regularity of gait performance in the L-Myc CKO (N = 21 in ABR; N=11 in Catwalk) and control (N = 18 in ABR; N=33 in Catwalk) mice at P21. Despite L-Myc CKO mice has overall near normal development similar to control as shown in Figure 1–3, both the auditory and vestibulo-motor function are detected abnormal at P21 compared to control (A, B). The ABR demonstrates a significantly worse hearing than the control in the L-Myc CKO mice (A, p<0.05). The L-Myc CKO mice also suffers from gait abnormality as shown with the significant decrease in the gait regularity compared to control (B, p<0.015). Note that the three survived P21 N-Myc CKO mice are assessed for the ABR and Catwalk, but no detectable ABR response are found at any frequency or sound level tested and are unable to walk in the Catwalk set-up and therefore data not included in the Figure 5. Error bars are standard error of the mean.