Fig. 2.
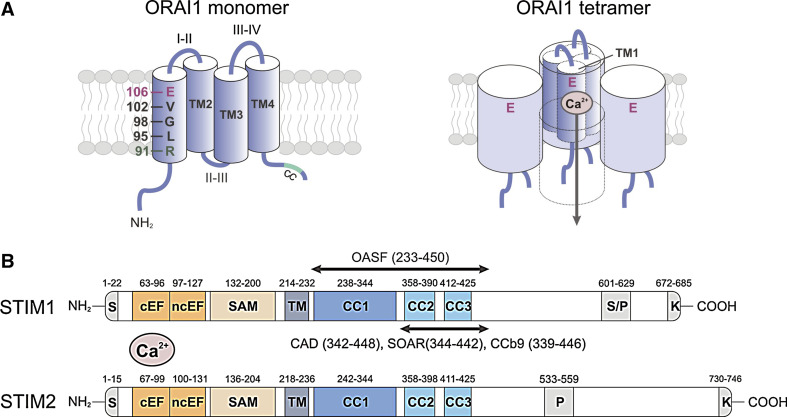
Molecular structure of ORAI1 and STIM1. a ORAI1 is a tetraspanning plasma membrane protein that contains intracellular N- and C-termini (NT, CT), two extracellular loops (I–II, III–IV), and an intracellular loop (II–III; left panel) [8–10]. A coiled-coil (CC) domain in the CT of ORAI1 mediates STIM1 binding and is required for CRAC channel activation [54]. ORAI1 is the pore-forming subunit of the CRAC channel [12–14]. The first transmembrane domain (TM1) of ORAI1 contains several residues that line the channel pore and mediate important CRAC channel functions. Glutamate (E) 106 provides a high-affinity Ca2+ binding site in the channel lumen and is responsible for the high Ca2+ selectivity of the CRAC channel [12–14]. V102 and R91 in the middle and at the cytoplasmic end of TM1, respectively, were proposed to form the channel gate that regulates Ca2+ permeation through the CRAC channel [19, 21]. G98 may function as a molecular hinge that allows the channel to open and close [19]. Functional CRAC channels are formed by assembly of four ORAI1 subunits (right panel) [22–24]. Four TM1 domains are thought to line the channel pore [11, 15], each contributing one E106 residue to form the Ca2+ binding site and Ca2+ selectivity filter [12–14, 16]. In this figure, the fourth ORAI1 subunit is removed to reveal the Ca2+ permeation pathway. b STIM1 and STIM2 are single-pass membrane proteins whose N- and C-termini are located in the lumen of the ER and the cytoplasm, respectively [39]. The NT of STIM1 contains a canonical EF-hand (cEF) that is paired with a noncanonical EF-hand (ncEF) [42]. The cEF hand domain is required for sensing the ER Ca2+ concentration and mutations of acidic residues within it result in impaired Ca2+ binding and constitutive CRAC channel activation independently of ER Ca2+ store depletion [32, 35, 43]. The CT of STIM1 and STIM2 contains two strong (CC1, CC2) and one weak (CC3) coiled-coil domains, which mediate STIM oligomerization upon store depletion. CC2 and CC3 are part of a minimal CRAC channel activation domain (CAD, also called STIM ORAI activating region (SOAR) or coiled-coil domain b9 (CCb9)), which directly binds to ORAI1 to activate CRAC channels [49, 51, 52]. The longer ORAI1-activating short fragment (OASF) also activates CRAC channels [53]. The lysine-rich region at the very CT is required for the recruitment of STIM1 to the plasma membrane (PM) by interacting with negatively charged phospholipids in the PM [59]. CC coiled-coil, EFh EF-hand, K lysine-rich, SAM sterile alpha motif, S signal peptide, S/P serine/proline-rich, TM transmembrane