Fig. 1.
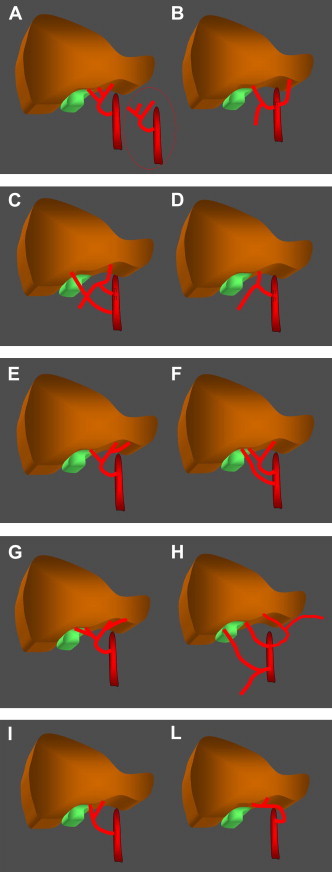
Classification of hepatic artery variants according to Michels. A. Type I is characterized by the presence of a middle hepatic artery that arises from the left or right branch of the proper hepatic artery. B. In type II, the common hepatic artery gives rise to the gastroduodenal and right hepatic arteries, and the left branch is replaced by the left gastric artery. C. In type III, the common hepatic artery gives rise exclusively to the gastroduodenal and left hepatic arteries. The right hepatic artery is replaced by the superior mesenteric artery. D. Type IV – the common hepatic artery divides to form the gastroduodenal and middle hepatic arteries. E. Type V is characterized by the presence of a left accessory hepatic artery that arises from the left hepatic artery. F. Type VI is characterized by the presence of a right accessory hepatic artery that arises from the superior mesenteric artery. G. In type VII there are right and left accessory hepatic arteries. H. Type VIII is a combination of substituted arteries (right or left) plus and inverted accessory artery. I. Type IX – the hepatic artery is replaced by the superior mesenteric artery. L. Type X – the hepatic artery is replaced by the left gastric artery.
