Fig. 1.
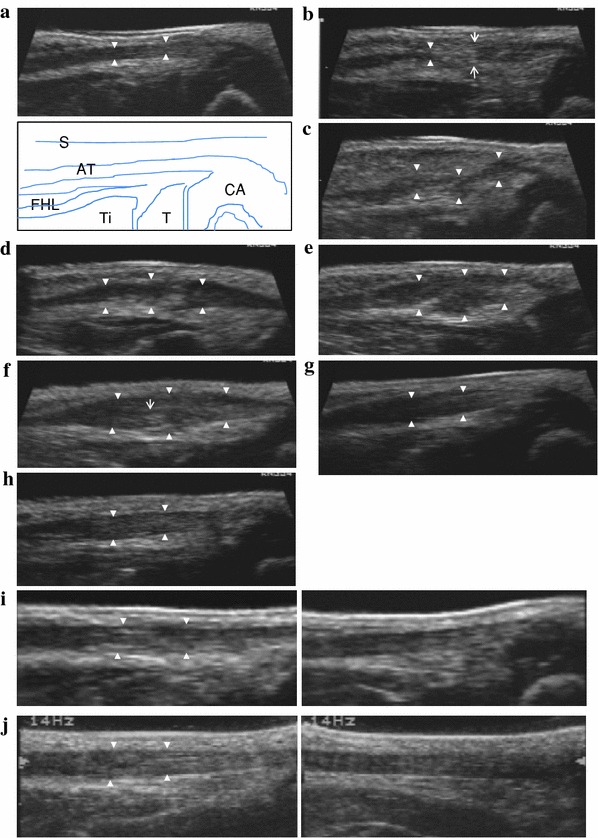
a Before tenotomy. Case 1 at two and a half months after birth. The Achilles tendon is clearly depicted as a low-echo region (solid white triangles). AT Achilles tendon, CA calcaneus, T talus, Ti tibia, FHL flexor hallucis longus, S skin. b 1–2 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at three months after birth and at 14 days after tenotomy. Solid white triangles show the proximal edge. White arrows show tenotomy portion. The gap zone is of mixed echogenicity. c 2–3 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at three months and one week after birth and at 21 days after tenotomy. Solid white triangles show that the lesion continued to be visible as a low echo. The gap is filled with irregular hypoechoic tissue. d 3–4 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at three and a half months after birth and at 28 days after tenotomy. Continuity of the tendon is identified. A bulbous appearance of the gap after tenotomy can be seen. e 4–6 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at three months and three weeks after birth and at 35 days after tenotomy. The united portion (solid white triangles) appears swollen. f 8–12 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at five months after birth and at 70 days after tenotomy. The united portion (solid white triangles) continues to thicken up to 8–12 weeks after tenotomy. The fibers are seen to display a linear configuration (narrow white arrow). g 14–16 weeks after tenotomy. Case 1 at six and a half months after birth and at 112 days after tenotomy. The healed portion (solid white triangles) begins to decrease in size. h Six months after tenotomy. Case 1 at eight and a half months after birth and at 169 days after tenotomy. The decease in size continued into the sixth month. Homogeneous tendon fibers are observed within the gap (white solid triangles). i One year after tenotomy. Case 1 at one year and two months after birth and at 358 days after tenotomy. Left shows the affected side and right the nonaffected side in the same case. The thickness does not differ much from that on the nonaffected side. The arrangement of tendon fibers within the gap is not similar at all to that on the normal side. j Two years after tenotomy. Case 1 at two years and three months after birth and at 719 days after tenotomy. Left shows the affected side and right the nonaffected side in the same case. Slight irregularity in the internal structure persists when compared with the nonaffected side
