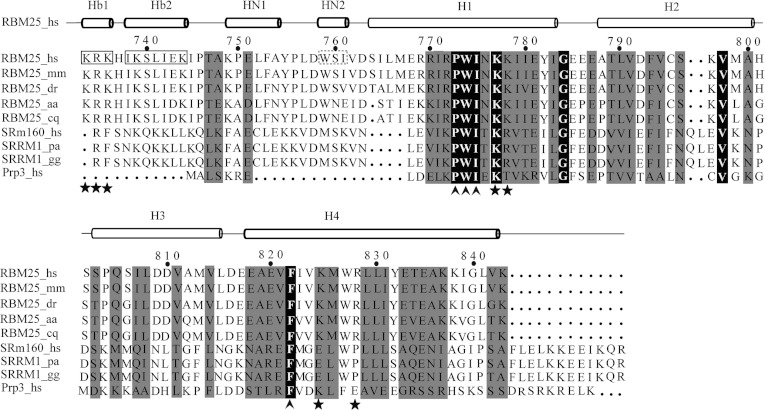
Figure 2. Sequence alignment of the RBM25 PWI domain with its homologues.
The following sequences were aligned using ClustalW2 (http://www.genome.jp/tools/clustalw): Homo sapiens (hs) RBM25 (NP_067062.1, NM_021239.2), Mus musculus (mm) RBM25 (NP_081625.3, NM_027349.3), Danio rerio (dr) RBM25 (NP_956084.1, NM_199790.1), Aedes aegypti (aa) RBM25 (XP_001649953.1, XM_001649903.1), Culex quinquefasciatus (cq) RBM25 (XP_001850266.1, XM_001850214.1), Homo sapiens (hs) SRm160 (NP_005830.2, NM_005839.3), Pongo abelii (pa) SRRM1 (NP_001126712.1, NM_001133240.1), Gallus gallus (gg) SRRM1 (NP_001026665.1, NM_001031494.1) and Homo sapiens (hs) Prp3 (NP_004689.1, NM_004698.2). The box highlights the flanking basic regions Hb1 and Hb2. The broken box highlights the 310-helix (HN2). The highly conserved residues Pro-Trp-Ile and phenylalanine are labelled with an upwards-pointing chevron. The contact residues for RNA/DNA binding are labelled with a star.