Fig 1.
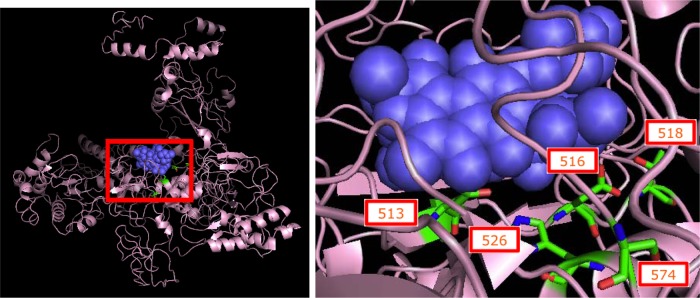
Mutated residues in the RNA polymerase β-subunit. (Left panel) Thermus aquaticus RNA polymerase β-subunit (pink diagram) with bound rifampin (purple spheres), the parent compound of rifaximin. (Right panel) A magnified view of bound rifampin and the T. aquaticus equivalents of the 5 amino acid codons (shown as RBG stick models) that were found to be mutated in our rifaximin resistant E. coli strains. All five codons occur close to the binding pocket of rifamycins; 3/5 codons (513, 516, and 526) are known to interact directly with the antibiotic and affect its binding (22). Image of 1I6V (22) created using The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (version 1.5.0.4; Schrödinger, LLC).
