Fig 5.
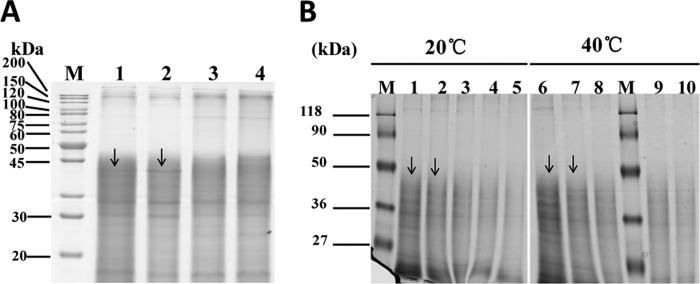
Bmp1 protein acts in the intestinal tissues. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protease degraded the intestinal tissue in vivo. We fed the Cry5Ba protein, Bmp1 protein, and Cry5Ba-Bmp1 combination separately to nematodes and then isolated the intestinal proteins. The profiles of the intestinal proteins were detected by SDS-PAGE analysis. Lanes: M, molecular mass standards; 1, intestinal protein of C. elegans observed by using the ddH2O test; 2, intestinal protein of C. elegans observed by using the crystal protein Cry5Ba test; 3, intestinal protein of C. elegans observed by using the Bmp1 protein (448.4 μg/ml) test; 4, intestinal protein of C. elegans observed by using the crystal protein Cry5Ba (221.7 μg/ml)/Bmp1 protein (224.4 μg/ml) mixture test. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis shows the protease degraded the intestinal tissue in vitro. We incubated the Bmp1 protein with the intestinal protein of normal C. elegans at 20 and 40°C in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) for 40 min. Lanes: M, molecular mass standards; 1 and 6, intestinal protein; 2 and 7, Bmp1 protein and intestinal protein at a ratio of 1:2 (wt/wt); 3 and 8, Bmp1 protein and intestinal protein at a ratio of 2:1 (wt/wt); 4 and 9, Bmp1 protein and intestinal protein at a ratio of 5:1 (wt/wt); 5 and 10, Bmp1 protein and intestinal protein at a ratio of 10:1 (wt/wt). The arrows point to the degradative proteins.
