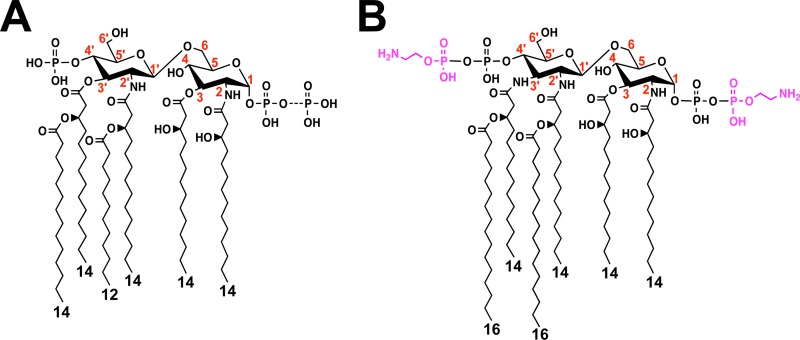
Fig 1.
Chemical structures of the lipid A domains of E. coli K-12 (A) and C. jejuni (B). The dashed bonds indicate variable modifications of lipid A, and the lengths of acyl chains are shown. In wild-type E. coli, an additional phosphate group can be attached at the 1 position (49). In C. jejuni, the lipid A disaccharide backbone is modified at the 1 and 4′ positions with phosphoethanolamine (magenta), and the glucosamine disaccharide backbone can be replaced with the analogue 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxy-d-glucopyranose, resulting in two or three additional amide-linked acyl chains compared to E. coli (9). The numbers in red indicate the positions on the disaccharide backbone of lipid A.