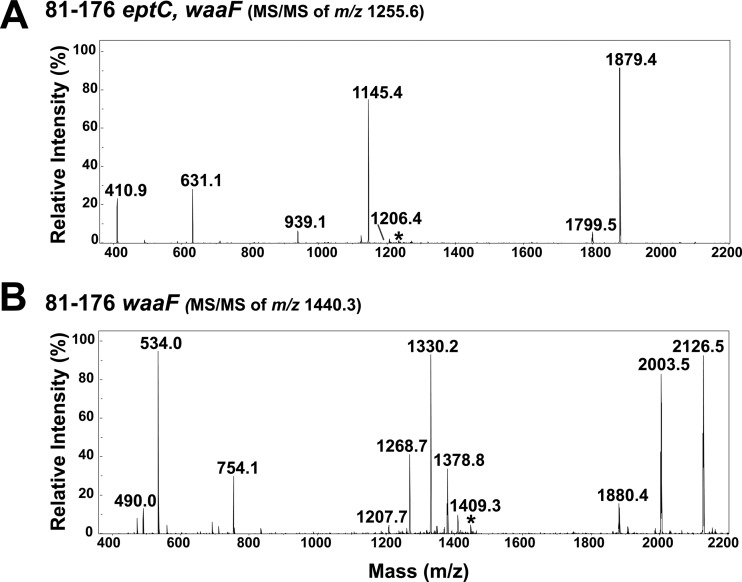
Fig 3.
LC-ESI–MS-MS of precursor ion m/z 1,255.6 (2−) from 81-176 eptC waaF (A) and precursor ion m/z 1,440.3 (2−) from 81-176 waaF (B) LOS. (A) Upon collisional activation, unmodified precursor ion m/z 1,255.6 (81-176 eptC waaF) yields several characteristic fragment ions, with the two most prominent, m/z 631.1 and 1,879.4, arising from cleavage of the Kdo-lipid A glycosidic bond, releasing the truncated inner core domain and the lipid A moiety. The other dominant ion observed, m/z 1,145.4, is consistent with the loss of one Kdo sugar. All ion fragments lack pEtN modification. (B) Upon collisional activation, pEtN-modified precursor ion m/z 1,440.3 (81-176 waaF) yields several characteristic fragment ions, m/z 1,378.8, 1,330.2, and 1,268.7, arising from the loss of one pEtN moiety, the loss of one Kdo group, or the loss of one pEtN and one Kdo group, respectively. The ions of m/z 2,126.5 and 754.1 are consistent with a lipid A-Kdo glycosidic cleavage, similar to that seen in unmodified LOS but modified with pEtN. The ion of m/z 533.9 confirms that one of the pEtN modifications remains on the heptose-plus-Kdo sugar substructure of the inner core domain, according to the proposed fragmentation pathway (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). The selected precursor ions are labeled with asterisks. The results agree between at least two experimental replicates of a single biological sample.