Corrections to probing the reaction mechanism of spore photoproduct lyase (SPL) via diastereoselectively labeled dinucleotide SP TpT substrates
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133 (27), pp 10434–10447 DOI: 10.1021/ja110196d
Linlin Yang,† § Gengjie Lin,† § Degang Liu,† Karl J. Dria, † Joshua Telser,|| and Lei Li †‡*
Page 10443: After carefully calibrating the 5′-dA and SP repair products generated from the wild-type spore photoproduct lyase (SPL) reaction, it was found that 3 equivalents of SAM support 5.4 turnovers upon a 3 hr enzyme reaction, not the 12 turnovers reported in Fig. 9A. The reported 5′-dA consumption in Fig. 9B was due to an unknown contaminant enzyme, but not the SPL activity to re-generate the S-adenosylmethionine. The corrected description of the reactivity of the wild-type SPL enzyme can be found in the following paper: Linlin Yang, Gengjie Lin, Renae S. Nelson, Yajun Jian, Joshua Telser, and Lei Li, Biochemistry, 2012, 51 (36), pp 7173–7188.
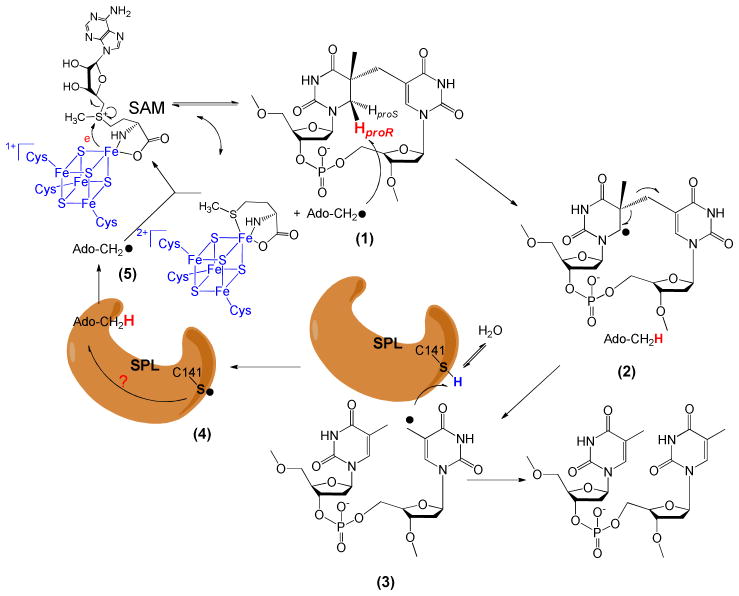
Page 10445: We are indebted to the cordial suggestion from Professor John-Stephen Taylor at the Washington University at St. Louis that the stereo-configuration of SP shown in Fig. 10 is not correct. The corrected Fig. 10 is shown below.
Figure 10.
Newly proposed reaction mechanism for SPL catalyzed SP dimer repair. The 5′-dA radical generated from SAM reductive cleavage reaction takes the 6-HproR atom to yield a C6 radical on SP, the SP methylene bridge subsequently undergoes a homolytic cleavage to give a thymine methyl radical. (Note: This allyl radical is likely to delocalize to the thymine aromatic ring; the current drawing as a methyl radical is a simplified model to facilitate discussion) This radical abstracts an H atom back from an unknown protein residue, presumably C141, to generate a thiyl radical, releasing the repaired TpT. This thiyl radical either takes an H-atom back from the 5′-dA directly, or it reacts with other protein residues before the 5′-dA is re-oxidized to the radical form again. The resulting 5′-dA radical recombines with methionine to regenerate SAM and finish one catalytic cycle.