Fig 2.
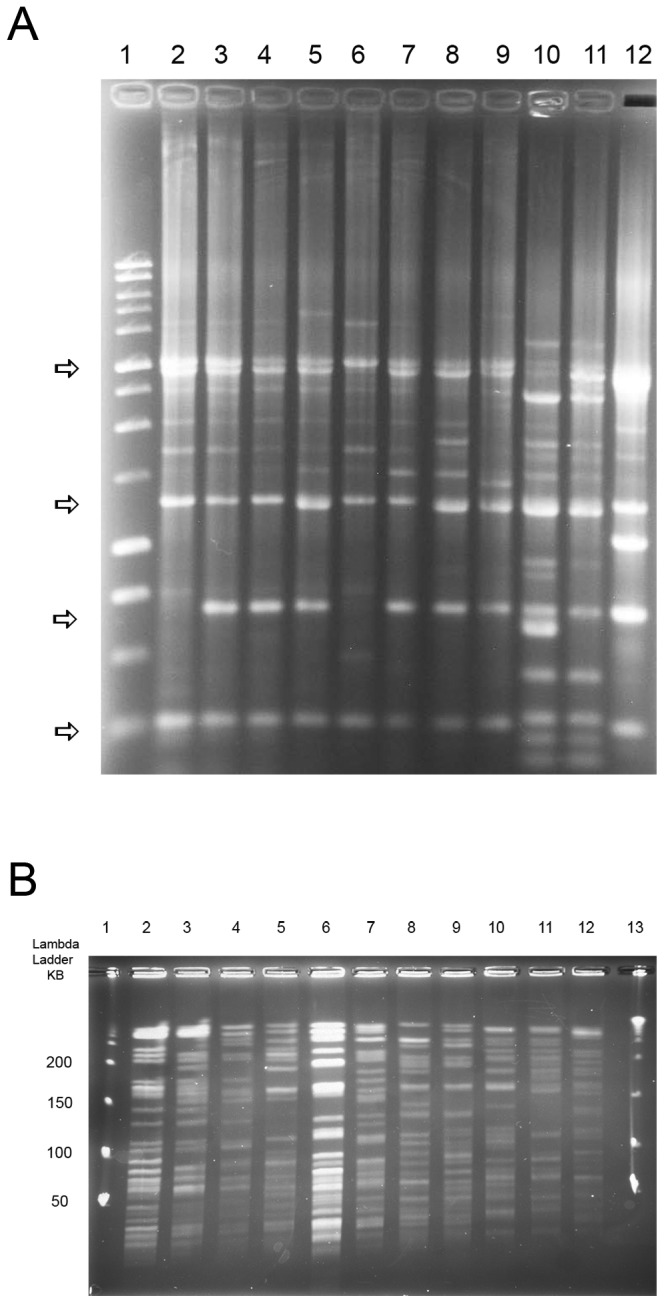
(A) rep-PCR of representative isolates from 9 different VNTR types of M. intracellulare. Note the overall similarity of the four major bands of M. intracellulare (marked by the arrows) despite isolates from multiple different VNTR types. Lane 1, 1-kb ladder; lane 2, type 5; lane 3, type 7; lane 4, type 11; lane 5, type 16; lane 6, type 24; lane 7, type 38; lane 8, type 36; lane 9, type 37; lanes 10 and 11, M. chimaera controls; lane 12, type 34. Lanes 2 to 9 and lane 12 are M. intracellulare. (B) PFGE using XbaI of representative isolates from the same 9 VNTR types of M. intracellulare and the two M. chimaera controls studied by rep-PCR for panel A. Note the overall difference of isolates from different VNTR types which were not as apparent with rep-PCR (A). Lanes 1 and 13, λ ladder; lane 2, type 5; lane 3, type 7; lane 4, type 11; lane 5, type 16; lane 6, type 24; lane 7, type 38; lane 8, type 36; lane 9, type 37; lanes 10 and 11, M. chimaera; lane 12, type 34. Lanes 2 to 9 and lane 12 are M. intracellulare.
