Figure 7.
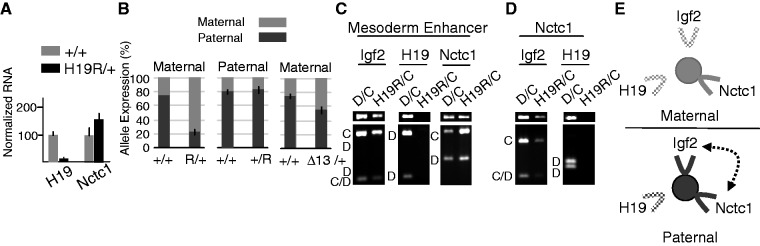
Nctc1 expression, imprinting and chromatin loop structures are altered on maternal H19R chromosomes. (A) Transcription of H19 and Nctc1 in H19R/+ muscle cells was quantitated by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH RNA levels. Expression of each gene in wild-type (+/+) cells is set at 100. (B) Parent-of-origin specific expression of Nctc1 on H19R and on Δ13 chromosomes. To quantitate the effects of maternal inheritance of H19R, allele-specific expression was measured for RNAs isolated from D/C and of H19R/C neonates. To quantitate the effects of paternal inheritance of H19R, C/D and C/ΔICR pups were compared. To quantitate the effects of maternal inheritance of Δ13, allele-specific expression was measured for RNAs isolated from D/C and of Δ13/C neonates. (C–D) Chromatin was prepared from primary myocytes isolated from wild-type mice (D/C) and from mice carrying a maternally inherited copy of the H19R insertion mutation (H19R/C) and analyzed by 3C. (C) Interactions between the mesoderm enhancer and the Igf2, the H19 or the Nctc1 promoter regions. (D) Interactions between the Nctc1 promoter and the Igf2 or H19 promoter regions. (E) Summary of long-range interactions on maternal (top, gray) or paternal (bottom, black) H19R chromosomes. Maternal inheritance of the ICR insertion prevents H19 promoter interactions with the CME (filled circle) and with the Nctc1 promoter. See Figure 4 for additional details.
