Figure 3.
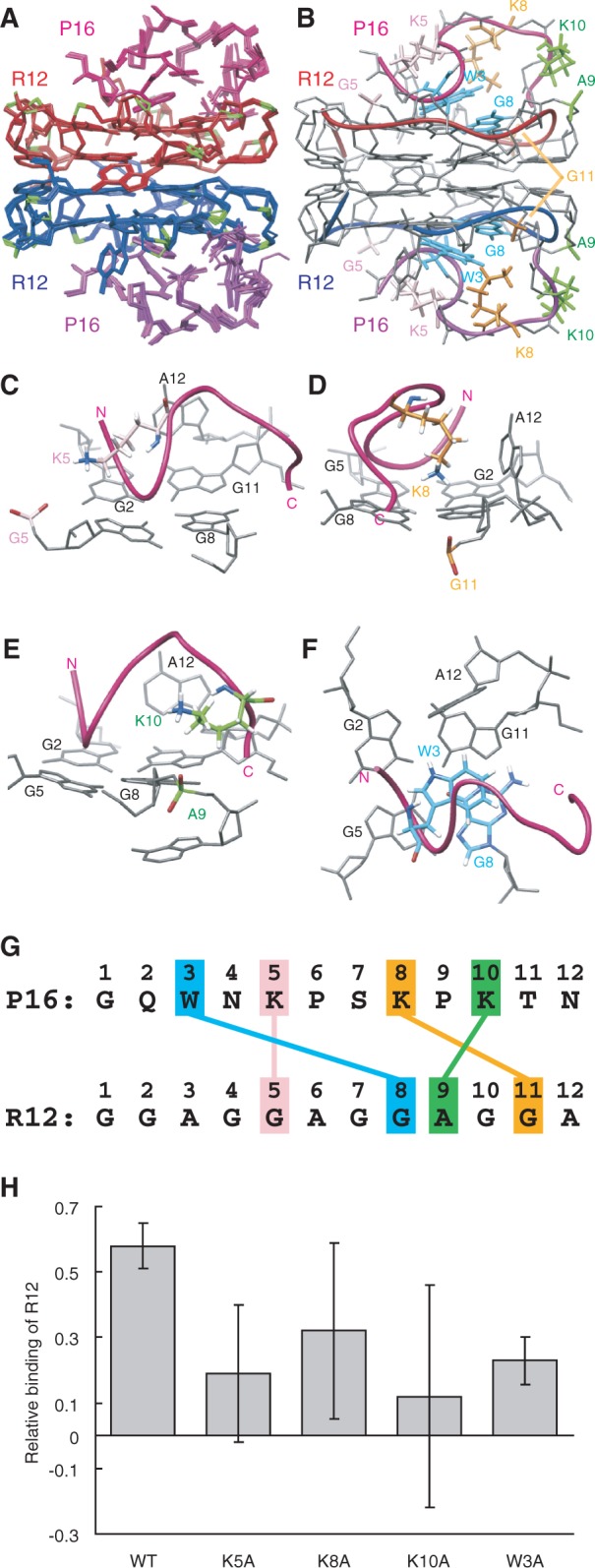
The structure of the R12:P16 complex. (A) NMR structure ensemble of the R12:P16 complex. The two R12 monomers are coloured red and blue, respectively, phosphate groups being coloured green. The two P16 monomers are coloured magenta and purple, respectively. (B) The representative structure with the lowest energy. The chains connecting the C3′ and C4′ atoms of each R12 monomer are indicated by red and blue tubes, respectively. The chains connecting the Cα atoms of each P16 monomer are indicated by magenta and purple tubes, respectively. The pairs K5 and G5, K8 and G11, K10 and A9 and W3 and G8 are coloured pink, orange, green and blue, respectively. (C–F) Close-up views of intermolecular interactions between K5 of P16 and G5 of R12 (C), K8 and G11 (D), K10 and A9 (E) and W3 and G8 (F), respectively. (G) Summary of interactions. The electrostatic interactions between K5 of P16 and G5 of R12, K8 and G11 and K10 and A9 and the stacking interaction between W3 and G8 are indicated. (H) The relative binding is shown for wild-type P16 and four mutant P16, in which either K5, K8, K10 or W3 was replaced by an alanine residue, respectively.
