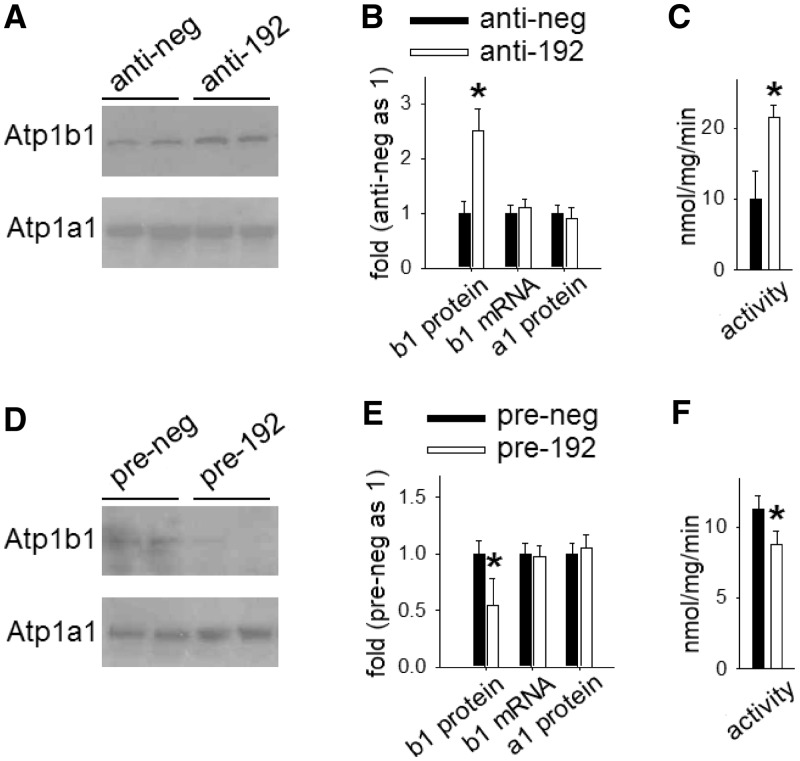
Figure 7.
Atp1b1 expression and membrane-bound Na+/K+-ATPase activity in human kidney cells is regulated by miR-192. Cultured human renal epithelial cells were transfected with 100 nM anti-miR-192 oligonucleotides for miR-192 knockdown and pre-miR-192 oligonucleotide for miR-192 over-expression and their respective scrambled control oligonucleotides (anti-neg and pre-neg). Cells were harvested after 48-h incubation period. Images on the left (A and D) show western blots for Atp1b1 and Atp1a1; graphs on the right represent quantification of Atp1b1 and Atp1a1 protein or mRNA expression and Na+/K+-ATPase activity. (A–C) Knocking down miR-192 resulted in up-regulation of Atp1b1 protein as well as increased membrane-bound Na+/K+-ATPase. mRNA levels of Atp1b1 and protein levels of Atp1a1 were not affected. n = 6–7, *P < 0.05 versus control. (D–F) Over-expressing miR-192 resulted in down-regulation of Atp1b1 protein as well as decreased membrane-bound Na+/K+-ATPase activity, without affecting Atp1b1 mRNA or Atp1a1 protein expressions. n = 6–7, *P < 0.05 versus control.