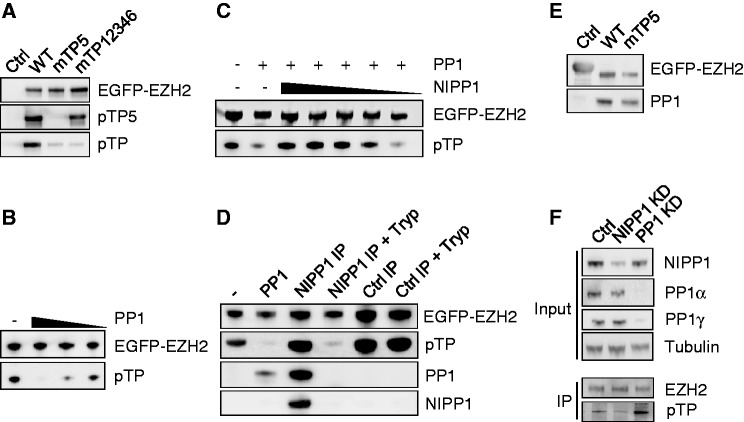
Figure 5.
NIPP1 inhibits the dephosphorylation of EZH2 by PP1. (A) EGFP (Ctrl) or the indicated EGFP-EZH2 variants were affinity purified by EGFP trap and examined for pTP and TP5 phosphorylation by immunoblotting. (B) Dephosphorylation of EZH2 by PP1. EGFP-EZH2 was immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cell lysates and in vitro dephosphorylated using PP1 (1.5 µM, 500 nM and 166 nM) that was purified from rabbit skeletal muscle. Remaining phosphorylation levels were analyzed by immunoblotting with pan-pTP antibodies. (C) Same as in (B, 500 nM PP1) with the addition of decreasing amounts of recombinant His-NIPP1 (4.5 µM–1.5 µM–500 nM–166 nM–55 nM). (D) EGFP-EZH2 was purified by EGFP trap and incubated as such (−), with 500-nM skeletal muscle PP1 or with the immunoprecipitated EGFP-NIPP1/PP1 complex, before and after trypsinization (Tryp). As a control, an EGFP-trap of EGFP-βGal was used (Ctrl IP). Dephosphorylation of EZH2 was examined by immunoblotting with pan-pTP antibodies. The presence of NIPP1 and PP1 was also verified by immunoblotting. The PP1 antibody does not recognize trypsin-pretreated PP1 because of the removal of the C-terminal epitope. Trypsinolysis during the phosphatase assay was prevented by the addition of soybean trypsin inhibitor. (E) EGFP-βgal (Ctrl) or EGFP-EZH2 (WT or mTP5) were immunoprecipitated out of HEK293T cell lysates and investigated for associated PP1 by immunoblotting. (F) Phosphorylation of EZH2 on TP-dipeptide motifs was visualized by immunoblotting after immunoprecipitation of endogenous EZH2 from nocodazole-arrested HeLa cells treated with RNAi for NIPP1, PP1 (α + γ isoform) or a scrambled Ctrl.