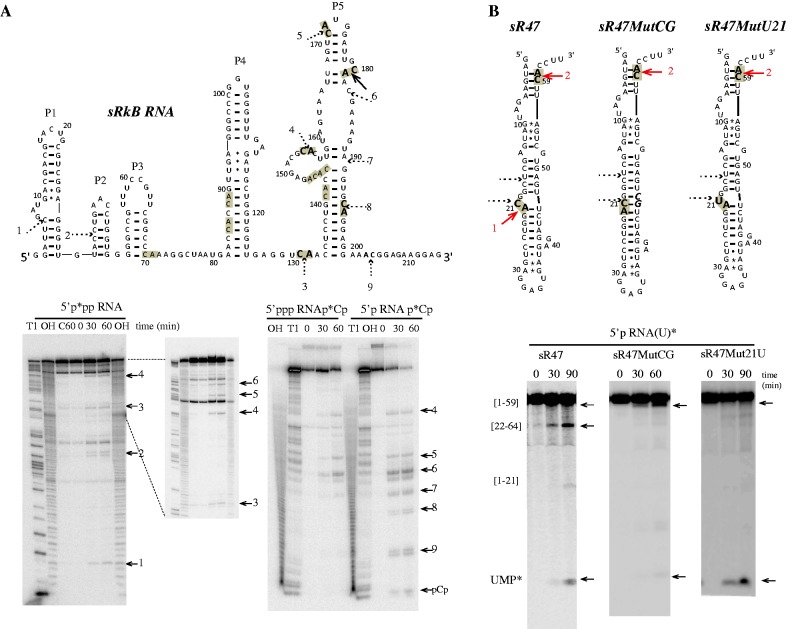
Figure 5.
In vitro activity of Pab-aCPSF1 on sRkB and sR47 variant RNA substrates. (A) Cleavage sites on the sRkB map are indicated by solid and dotted arrows for strong and weak, respectively. The cleavage sites are numbered from 1 to 9 and the 11 CA dinucleotides of sRkB RNA are highlighted in grey (Top). The kinetic analysis of cleavage of the 5′p*pp RNA, 5′ppp RNAp*Cp and 5′p RNAp*Cp sRkB substrates at 65°C is shown (Bottom). (B) Cleavage sites induced by Pab-aCPSF1 on the sR47, sR47MutCG and sR47Mut21U maps (Top). The CA dinucleotides are highlighted in grey and the cleavage sites are indicated by red arrows. The sR47MutCG and the sR47Mut21U mutants possess an extra CG dinucleotide (bold italic characters, forming base pairs with G20 and C21) and a U at position 21, respectively. The CG insertion impedes cleavage at C21 and reduced the exonucleolytic degradation pathway as shown by the kinetic analyses of uniformly labeled sR47 and sR47MutCG (5′p RNA(U)*). The replacement of the U by a C impedes cleavage at position 21 but does not affect the exonucleolytic degradation of 5′p sR47Mut21U (U)* (Bottom). See Figure 2 legend for symbols.