Fig 1.
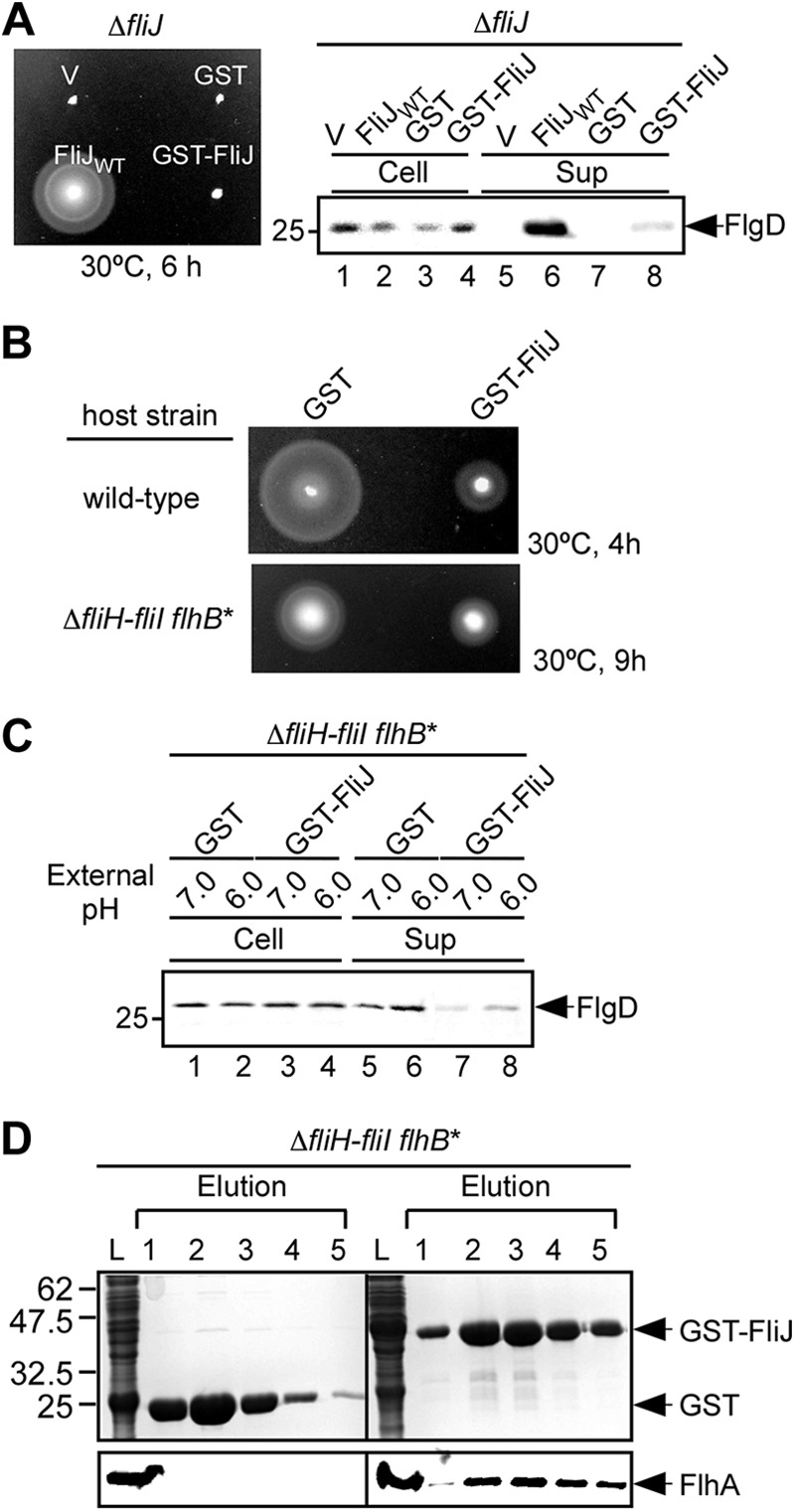
Interaction of GST-FliJ with FlhA. (A) Motility assays of MKM40 (ΔfliJ) transformed with pTrc99AFF4 (V), pGEX6p-1 (GST), pMM404 (wild-type FliJ, indicated as FliJWT), or pMMJ1001 (GST-FliJ) in soft agar plates. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 6 h. (B) Dominant-negative effect of GST-FliJ on motility of wild-type cells (upper panel) and the ΔfliH-fliI flhB(P28T) bypass mutant (lower panel). The motility of SJW1103 (wild type) and MMHI0017 (ΔfliH-fliI, flhB*) transformed with pGEX-6p-1 (GST) or pMMJ1001 (GST-FliJ) in soft agar plates was evaluated. (C) Effect of external pH on FlgD secretion by the ΔfliH-fliI flhB(P28T) bypass mutant. Immunoblotting was performed with the polyclonal anti-FlgD antibody of whole-cell and culture supernatant fractions prepared from the ΔfliH-fliI flhB(P28T) bypass mutant overexpressing GST or GST-FliJ grown at external pH values of 6.0 and 7.0. (D) Pulldown assays by GST affinity chromatography. The soluble fractions (indicated as L) from the ΔfliH-fliI flhB(P28T) bypass mutant overproducing GST or GST-FliJ were loaded onto a GST column. After being washed with 10 ml of PBS, the proteins were eluted with a buffer containing 10 mM reduced glutathione. The eluted factions containing GST or GST-FliJ were analyzed by CBB staining (upper panels), while the eluted FlhA protein was done by immunoblotting with polyclonal anti-FlhAC antibody (lower panels).
