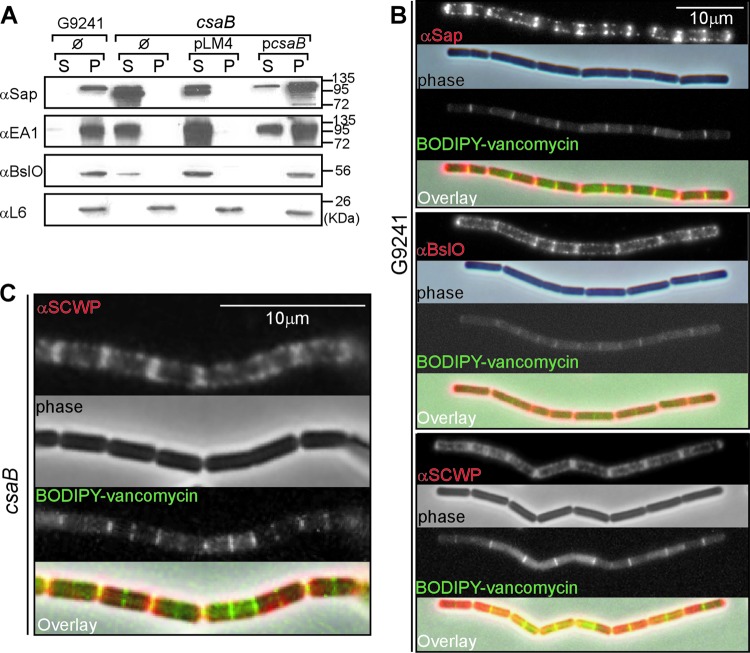
Fig 3.
The B. cereus G9241 csaB mutant cannot assemble S-layer proteins and S-layer-associated proteins into the bacterial envelope. (A) B. cereus G9241 wild-type and csaB mutant were grown to exponential phase in BHI broth. Bacilli harbored no plasmid (Ø), the pLM4 vector, or the complementing plasmid pcsaB. Cultures were centrifuged to sediment vegetative bacilli (pellet [P]) and separate them from the extracellular medium (supernatant [S]). Proteins in both fractions were precipitated with TCA and analyzed by immunoblotting with rabbit antisera raised against purified recombinant Sap (αSap), EA1 (αEA1), BslO (αBslO), and ribosomal protein L6 (αL6). The migratory positions of molecular mass markers on SDS-PAGE are indicated. (B) Immunofluorescence and phase-contrast microscopy images of wild-type B. cereus G9241 grown to exponential phase in BHI. Bacilli were stained with antisera specific for Sap, BslO, or SCWP and with secondary antibody conjugated to Alexa-Fluor 594 (red). To reveal the cell wall septa between adjacent bacilli, chains were stained with BODIPY-vancomycin (green), which binds the peptidoglycan precursor lipid II. (C) Immunofluorescence and phase-contrast microscopy images of csaB mutant B. cereus G9241 grown to exponential phase in BHI. Bacilli were stained with antisera specific for the SCWP (red) or with BODIPY-vancomycin (green). Data are representative of three independent experimental determinations.