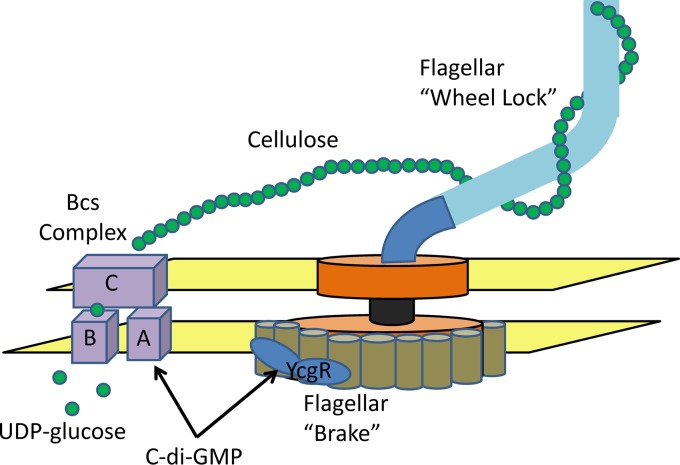
Fig 1.
c-di-GMP inhibits motility of S. Enteritidis by binding to two PilZ-containing proteins, YcgR and BcsA. Binding of c-di-GMP to YcgR functions as a flagellar “brake” by altering the rotation direction and frequency of the flagella, while an interaction of c-di-GMP with BcsA stimulates cellulose synthesis through the Bcs complex. Extracellular cellulose inhibits flagellar rotation, functioning effectively as a flagellar “wheel lock.”