Fig 3.
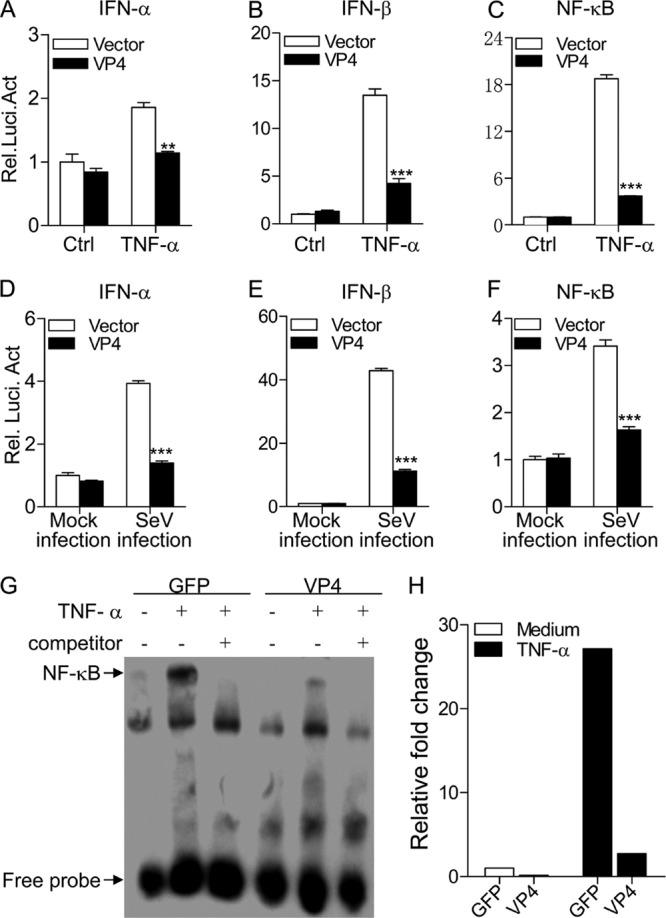
Expression of VP4 inhibits TNF-α- or SeV-induced activation of IFN-α, IFN-β, and NF-κB promoters. (A to C) Effects of VP4 on TNF-induced activation of IFN-α, IFN-β, and NF-κB promoters. HEK293T cells (2.0 × 105) were transfected with pEGFP-vp4 or empty vector (pEGFP-N1) as a control together with the indicated reporter plasmids. Eighteen hours after transfection, cells were treated with 20 ng/ml of TNF-α or medium as a control for 12 h before reporter activities were examined with a dual-specific luciferase assay kit. (D to F) Effects of VP4 on SeV-induced activation of IFN-α, IFN-β, and NF-κB promoters. HEK293T cells (2.0 × 105) were transfected with pEGFP-vp4 or empty vector as controls together with the indicated reporter plasmids. Eighteen hours after transfection, cells were mock infected or infected with SeV at an MOI of 10 for 24 h before reporter activities were examined with a dual-specific luciferase assay kit. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Data are represented as means ± SD; n = 3. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. (G) Impact of VP4 on TNF-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65. HEK293T cells (5.0 × 105) were transfected with pEGFP-vp4 or empty vector as a control. Twenty hours after transfection, cells were treated with 100 ng/ml of TNF-α or medium as controls for 45 min before crude nuclear proteins were extracted. The nuclear proteins were then subjected to EMSA for determining the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65. The detection of the NF-κB-oligonucleotide complex was performed using a Light Shift chemiluminescence EMSA kit. (H) The density of relative nuclear translocated NF-κB p65 bands in panel G was quantitated by densitometry and normalized to that of vector control. Results are representative of three independent experiments.
