Fig 5.
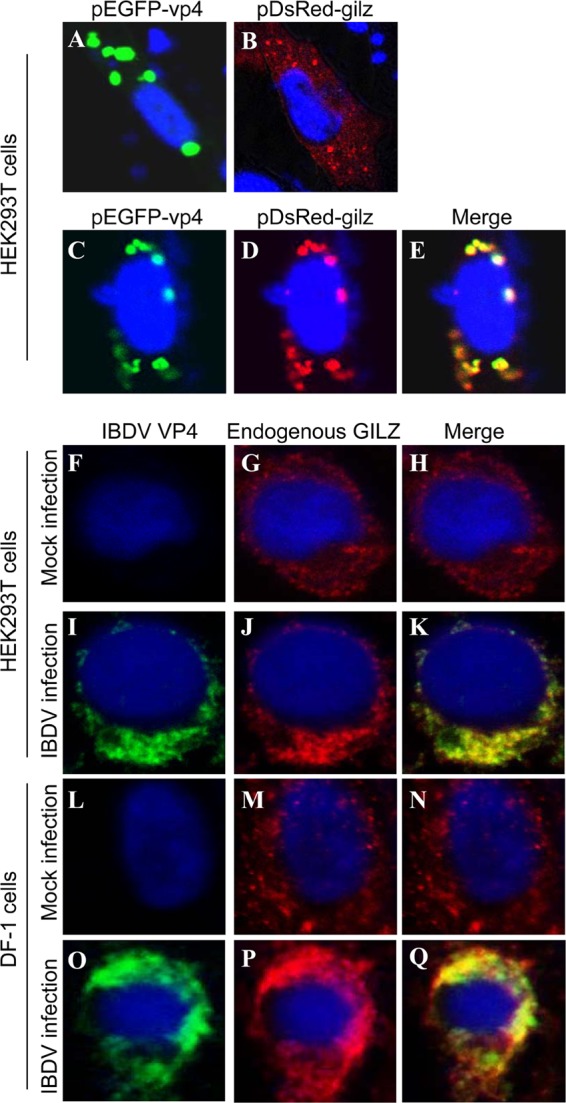
Colocalization of VP4 with GILZ in the cell. (A and B) Expression of exogenous VP4 (A) or GILZ (B) in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells (2 × 105) were seeded on 24-well plates with coverslips in the wells and cultured overnight. Cells were transfected with pEGFP-vp4 (A) or pDsRed-gilz (B). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were fixed and observed with a laser confocal scanning microscope. (C to E) Colocalization of VP4 with exogenous GILZ. HEK293T cells (2 × 105) were seeded on 24-well plates with coverslips in the wells and cultured overnight. Cells were transfected with both pEGFP-vp4 and pDsRed-gilz. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were fixed and observed with a laser confocal scanning microscope. (F to Q) Colocalization of IBDV VP4 with endogenous GILZ in IBDV-infected cells. HEK293T (F to K) or DF-1 (L to Q) cells were mock infected (F to H and L to N) or infected with IBDV Lx (I to K and O to Q) at an MOI of 10 and incubated for 3 h at 37°C. Twenty-four hours after IBDV infection, cells were fixed and probed with mouse anti-VP4 antibodies and rabbit anti-GILZ antibodies, followed by the FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody (green) and TRITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue) and were visualized under a fluorescence microscope.
