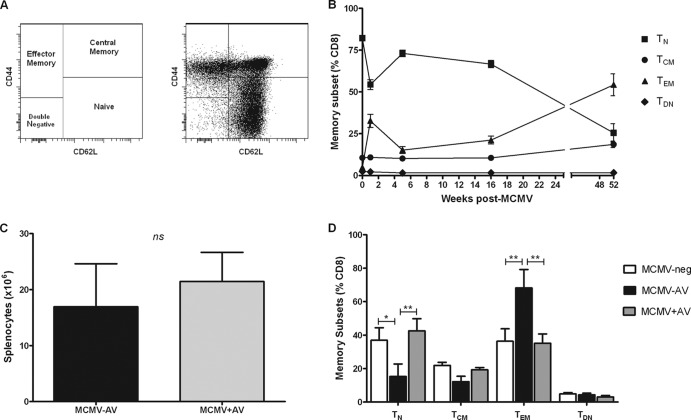
Fig 5.
Antiviral treatment restores the naïve and memory CD8+ T-cell pools to those seen in MCMV-neg mice. (A) Representative FACS plots of CD8+ T-cell memory subsets: naïve (TN) (CD44− CD62L+), central memory (TCM) (CD44+ CD62L+), effector memory (TEM) (CD44+ CD62L+), and double negative (TDN) (CD44− CD62L−) phenotypes. (B) Frequencies of naïve, central memory, effector memory, and intermediate CD8+ T cells following MCMV infection, where the numbers of mice range from 3 to 4 per time point (mean ± SEM). (C) The numbers of live splenocytes isolated from MCMV−AV (n = 6) mice 18 months postinfection and following 12 months of antiviral treatment (MCMV+AV) (n = 8). The data were analyzed by the two-way Mann-Whitney U test (ns, P > 0.05). (D) Frequencies of TN, TCM, TEM, and TDN CD8+ T cells are shown from spleen samples of MCMV-neg (n = 3), MCMV−AV (n = 3), and MCMV+AV (n = 4) groups of mice (mean ± SEM). The data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA plus Bonferroni's posttest correction (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).