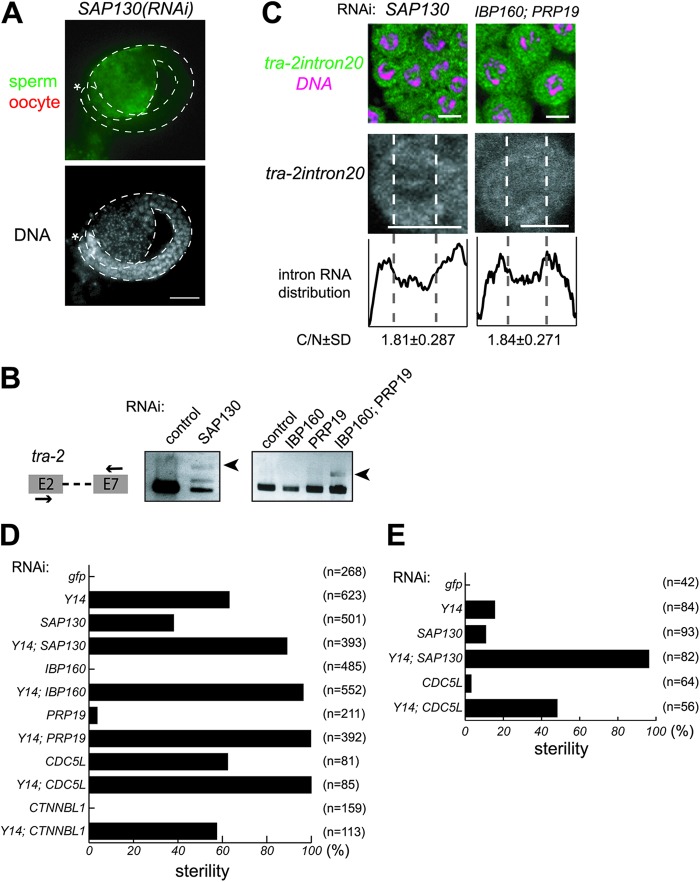
Fig 6.
The splicing factors required for the nuclear retention of unspliced RNAs and their interactions with Y14. (A) Gonad arms were dissected from SAP130(RNAi) hermaphrodites and stained with the anti-MSP antibody (green) and anti-RME-2 antibody (red) (top) and DAPI (bottom). Asterisks indicate the distal end of the gonad. Gonad is outlined by dashed lines. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) RT-PCR assays were performed to monitor tra-2 expression in animals subjected to RNAi as indicated. The primers used for amplification are schematically shown on the left. Arrowheads indicate unspliced tra-2 RNA. (C) In situ hybridization of mitotic cells within gonad arms dissected from SAP130(RNAi) and IBP160(RNAi); PRP19(RNAi) hermaphrodites. Cells were probed with tra-2 intron 20 (green), followed by DNA staining (magenta), shown as merged views (top). Separate views of single cells probed with the intron are also shown (middle). The intracellular distribution of the intron is shown as described in the legend to Fig. 3B (bottom). Scale bars, 4 μm. (D) Percent sterility caused by RNAi as indicated. (E) Percent sterility caused by indicated RNAi treatment in the background of the rrf-1(pk1417) mutation.