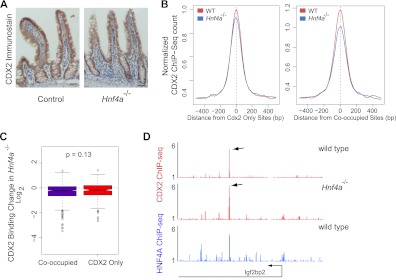
Fig 4.
HNF4A binding is dispensable for CDX2 occupancy of intestinal epithelial cell DNA. Binding of CDX2 was assessed in the absence of HNF4A. (A) CDX2 immunostaining confirms that its expression is unaffected in Hnf4a−/− intestines. (B) Composite ChIP-Seq plots of all regions bound only by CDX2 (left) or by both CDX2 and HNF4A (right). DNA occupancy of CDX2 is similar in wild-type and Hnf4a−/− cells, with a very minor diminution in binding in mutant cells. (C) In a site-for-site comparison of normalized ChIP-Seq tag counts, the minor changes in CDX2 binding are similar among sites bound only by CDX2 or by both TFs (Mann-Whitney test, P = 0.13). Box plots show the log2 fold difference of the normalized CDX2 ChIP-Seq read counts between WT and Hnf4a-null intestines, at cooccupied and CDX2-only binding sites. The middle bar indicates the median of the distribution, and the lower and upper edges represent 25% and 75% quartiles, respectively. Whiskers represent the lower (−1.5 × interquantile range) and upper (+1.5 × interquantile range) edges. Circles beyond the whiskers are outliers. (D) A representative data trace from chromosome 16 position 22120000 to 22180000 illustrates preserved CDX2 binding in Hnf4a−/− cells.