Table 4.
Impact of genotype calling algorithm on estimates of heritability from control–control samples
| Disease | Samples | No. of SNPs |
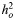 (SE) (SE) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard QC | ||||
| 1958A (I)/1958B (I) | 1076/1576 | 492893 | 0.00 (0.13) | 1.00 |
| 1958A (G)/1958B (I) | 1076/1576 | 492893 | 0.20 (0.14) | 0.13 |
| 1958A (I)/OECX (I) | 1076/2565 | 473047 | 0.04 (0.10) | 0.66 |
| 1958A (G)/OECX (I) | 1076/2565 | 466005 | 0.48 (0.10) | 1.9e-06 |
| 1958A (I)/QIMR (G) | 1076/1836 | 488150 | 0.53 (0.12) | 4.7e-06 |
| 1958A (G)/QIMR (G) | 1076/1836 | 472019 | 0.64 (0.12) | 1.0e-07 |
| Most stringent QC | ||||
| 1958A (G)/OECX (I) | 1076/2565 | 313076 | 0.04 (0.10) | 0.68 |
| 1958A (I)/QIMR (G) | 1076/1836 | 397802 | 0.08 (0.12) | 0.48 |
| 1958A (G)/QIMR (G) | 1076/1836 | 337695 | 0.16 (0.12) | 0.20 |
The 1958 cohort was split into a sample (1958A) for which genotypes had been called with both Illuminus (I) and with GenCall (G) and into a sample only called with Illuminus (1958B). The OECX sample is the OEC control samples with 1958 cohort controls removed. In this way, 1958A, 1958B and OECX are three independent control samples.
