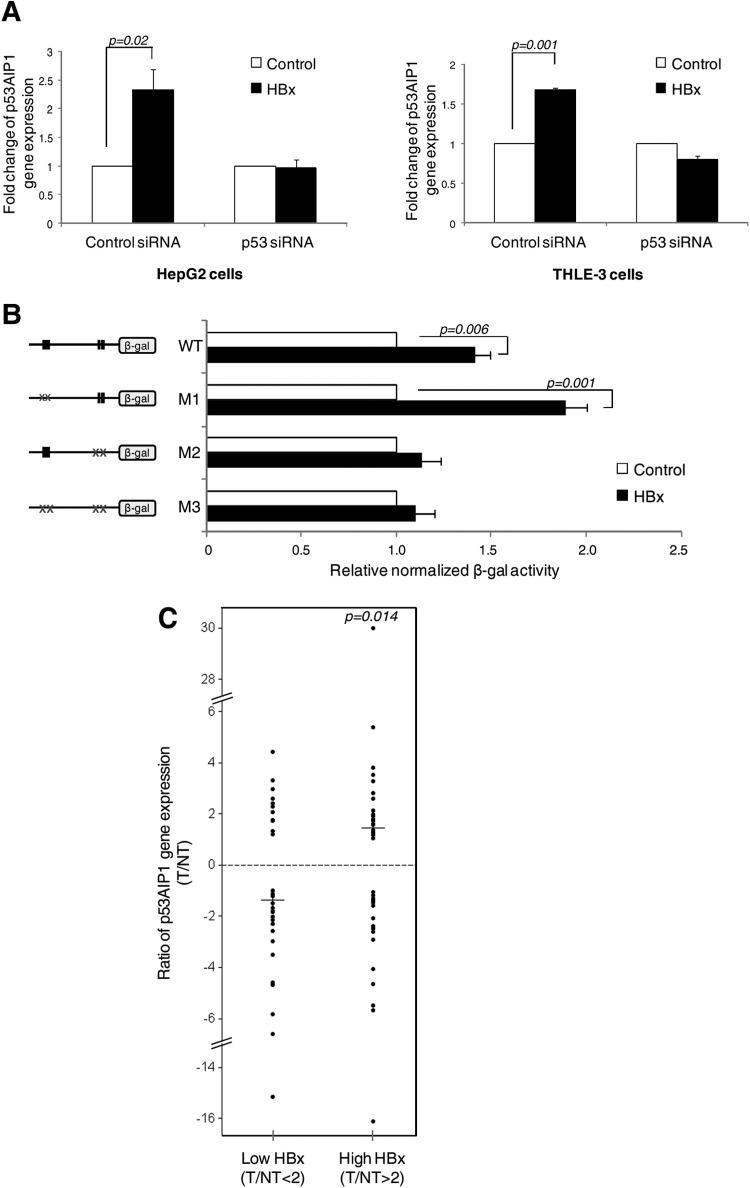
Fig 3.
A shift in p53 DNA binding directly results in a deregulated increase in p53AIP1 expression. (A) p53AIP1 expression in p53-specific or control siRNA-treated HBx and control HepG2 (left) and THLE-3 (right) cells measured by qPCR. (B) β-Gal activity of the indicated WT or mutant promoter constructs cotransfected with p53 in HBx or control Hep3B cells. The x axis shows a comparison of the normalized β-Gal activity of each construct in the presence or absence of HBx, and the difference is expressed as relative β-Gal activity in the presence of HBx versus β-Gal activity in the absence of HBx (i.e., control). (C) p53AIP1 gene expression and HBx protein status of T and paired adjacent NT samples from 78 HCC patients analyzed by qPCR and immunoblotting, respectively. The median ratios (horizontal lines) of p53AIP1 expression (T/NT) in patients with low (T/NT < 2) and high (T/NT > 2) HBx protein expression levels are shown.