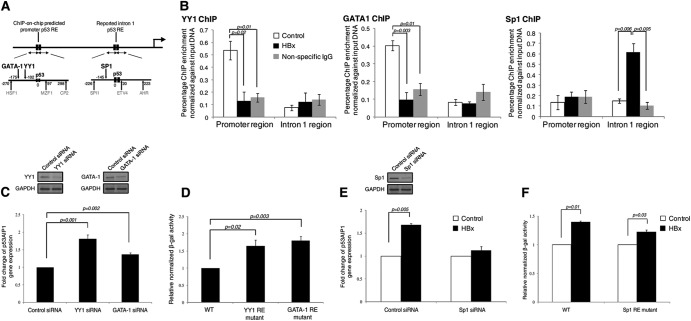
Fig 5.
Distinct transcription cofactors are differentially recruited by HBx and influence gene transcription. (A) MatInspector- and TRANSFAC-predicted promoter and intron 1 TFs and their positions relative to the respective p53 REs. p53-interacting TFs GATA-1, YY1, and SP1 are indicated in boldface. (B) ChIP-qPCR-validated YY1 (left), GATA-1 (middle), and Sp1 (right) occupancy in HBx and control THLE-3 cells using the respective specific antibodies. (C to F) Surrounding transcription cofactors modulate p53AIP1 expression. (C) Western blots showing efficient knockdown of YY1 (top left) and GATA-1 (top right) using specific siRNA. Depletion of YY1 or GATA-1 increases p53AIP1 expression in THLE-3 cells as measured by qPCR (bottom). (D) Mutation of YY1 or GATA-1 RE at the p53AIP1 promoter increases reporter activity in Hep3B cells. (E) (Top) Western blots showing efficient knockdown of Sp1 using specific siRNA. (Bottom) Depletion of Sp1 negates HBx-increased p53AIP1 expression in THLE-3 cells as measured by qPCR. (F) Mutation of the Sp1 RE at p53AIP1 intron 1 negates HBx-increased reporter activity in Hep3B cells. All error bars show standard errors of the mean from triplicate experiments.