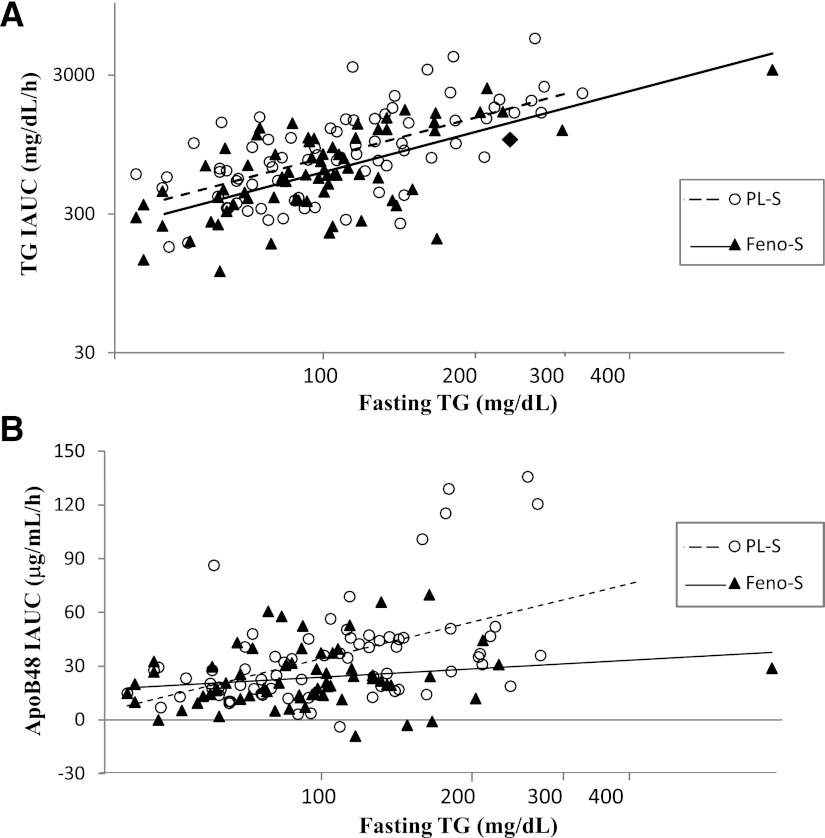
Figure 2.
Relationships between fasting plasma TG and the postprandial incremental excursions of plasma TG and apoB48. The fenofibrate effect on (log-transformed) IAUCs was analyzed by multiple regression with fenofibrate, sex, (log-transformed) day of study fasting TG, and fenofibrate × TG interaction as independent variables. For TG IAUC, the effect of fenofibrate was similar across the full range of day of study fasting TG (the solid and dashed regression lines are parallel) (A). The r value for the correlation between fasting TG and TG IAUC was 0.61 (P < 0.0001) for each group. In contrast, there was a significant interaction between day of study fasting TG levels and the effect of fenofibrate on the IAUC for apoB48 (the solid and dashed regression lines are not parallel) (B), whereby only participants with TG levels at and above the median had significant reductions in apoB48 IAUC (P = 0.003 for interaction; Table 2). Fasting TG and apoB48 IAUC were significantly correlated in the PL-S (r = 0.49; P < 0.001), whereas there was no significant relationship between fasting TG and apoB48 IAUC in the FENO-S group (r = 0.20; P = 0.11).