FIG. 3.
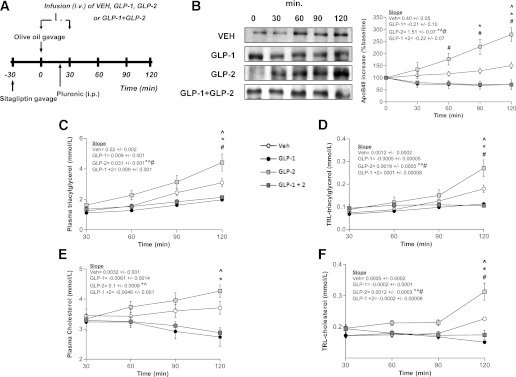
Inhibition of DPP-4 augments GLP-1 action, resulting in decreased postprandial lipemia in GLP-1/GLP-2–coinfused hamsters. A: Chow-fed hamsters received treatment with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin (intraperitoneal) 30 min prior to experiments, and then received an oral fat load followed by a 30-min intravenous infusion of either VEH, GLP-1, GLP-2, or GLP-1 and GLP-2; poloxamer was administered 20 min post–fat load (intraperitoneal). Blood was collected at 30, 60, 90, and 120 min to assess lipemia. B: A representative blot of TRL-apoB48 is shown along with a graph showing quantification of apoB48. Plasma (C) and TRL-TG (D) levels and plasma (E) and TRL-cholesterol (F) levels were quantified and represented in graphs (n = 4–5). Each graph represents the mean ± SEM at each time point for the given parameter. Calculated slopes are shown within each graph (n = 4–5; *P < 0.05 vs. GLP-1, #P < 0.05 vs. GLP-2, ^P < 0.05 vs. GLP-1 + GLP-2).
