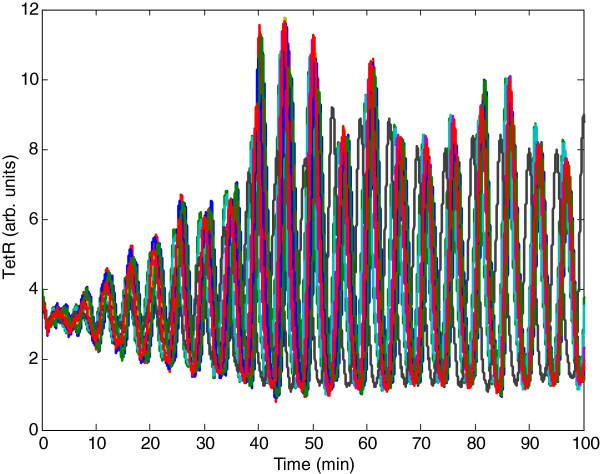
Figure 2.
Ten coupled genetic oscillators. The parameter values in (1), (2), and (3) are set as follows: αa = αb = αc = 216, αS = 20, μ = 1.2, μS = 1, n = 2, γS = 1, ηS = 2, βS = 0.1, βA = βB = βC = 1, γm = 6.9315, γp = 1.1552 and Qe = 0.09 [1]. Suppose the nonlinear stochastic coupled synthetic oscillators suffer from stochastic parameter fluctuations as shown in (8) with Δαa = Δαb = Δαc = 2.16, ΔαS = 0.2, ΔβA = ΔβB = ΔβC = 0.01, ΔβS = 0.001, ΔηS = 0.02, Δγm = 0.06, Δγp = 0.01, and ΔγS = 0.01. For the convenience of simulation, we assume that the extrinsic molecular noise v1~v10 is independent Gaussian white noise with a mean of zero and standard deviation of 0.02. It can be seen that coupled synthetic oscillators cannot achieve synchronization under these intrinsic kinetic parameter fluctuations and extrinsic molecular noise.